W
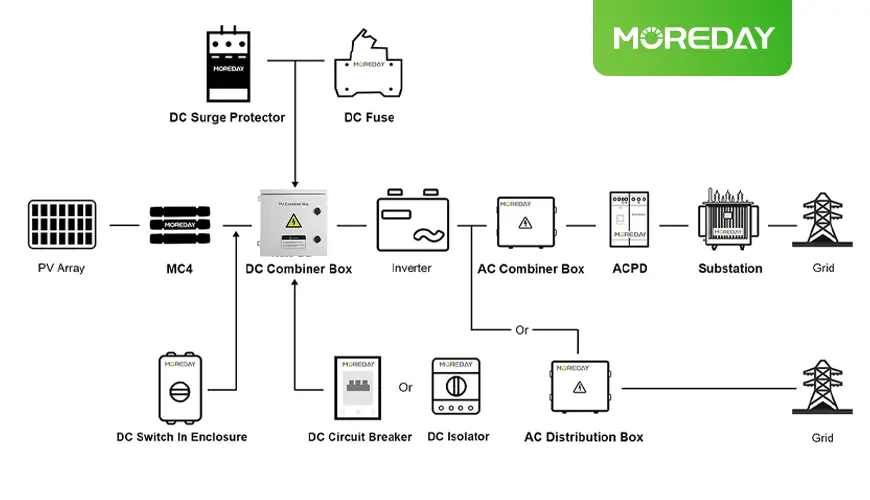
hen diving into the world of photovoltaic (PV) systems, you’ll encounter various components like PV combiner box, each playing a crucial role in harnessing solar energy efficiently. As the global demand for renewable energy sources continues to rise, solar power has emerged as a leading solution due to its sustainability and decreasing costs. PV systems, which convert sunlight into electricity, are becoming increasingly common in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. These systems consist of multiple interconnected components, each contributing to the overall functionality and efficiency of the setup.
One of the most important, yet often overlooked, components in a PV system is the PV combiner box. Despite its critical role, many people are unfamiliar with what a PV combiner box is and why it is essential for a well-functioning solar power system. This article aims to demystify the PV combiner box, exploring its definition, functionality, and the benefits it brings to PV installations.

What is a PV Combiner Box?
A PV combiner box, also known simply as a combiner box, is an essential component in photovoltaic (PV) solar power systems. It serves as a central point where the electrical outputs from multiple solar panel strings are combined into a single, manageable output that is then sent to an inverter. This inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which can be used to power homes, businesses, and other facilities.
Definition
In more technical terms, a PV combiner box is an electrical enclosure that houses various protective and connection devices. It is specifically designed for PV applications to ensure the efficient and safe aggregation of power from several solar strings. These boxes are typically installed between the solar panels and the inverter, playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the solar power system.
Basic Functionality
The primary function of a PV combiner box is to streamline the wiring and connection of multiple solar panels. In a typical solar array, each string of panels generates its own current, which needs to be combined with currents from other strings to create a single, more substantial output. The PV combiner box achieves this by collecting the outputs from each string and merging them into a single pair of cables that lead to the inverter.
Components of a PV Combiner Box
A PV combiner box is a critical component in solar photovoltaic (PV) systems, designed to consolidate the electrical output from multiple solar panel strings. Understanding the components within a PV combiner box is essential for appreciating its role in ensuring the safety, efficiency, and reliability of solar power systems. Here, we will explore the key components that make up a PV combiner box and their respective functions.
1. Fuses or Circuit Breakers
Fuses and circuit breakers are fundamental safety devices used in PV combiner boxes to protect the system from overcurrent conditions. Each string of solar panels is connected to the combiner box through a fuse or circuit breaker.
Fuses: These are sacrificial devices that melt and break the electrical connection when the current exceeds a certain threshold. They are simple, reliable, and cost-effective means of overcurrent protection.
Circuit Breakers: These are resettable devices that trip when the current exceeds a certain limit. Unlike fuses, circuit breakers can be reset after tripping, making them more convenient for maintenance and troubleshooting.
Both fuses and circuit breakers prevent electrical faults in one string from affecting the entire system, ensuring the safety and integrity of the solar array.
2. Surge Protection Devices (SPD)
Surge protection devices are crucial for protecting the PV system from voltage spikes, which can be caused by lightning strikes, switching operations, or other transient events. SPDs divert excess voltage away from the sensitive components of the solar power system, preventing damage and extending the lifespan of the equipment.
Type 1 SPDs: These are designed to protect against direct lightning strikes and are typically installed at the service entrance.
Type 2 SPDs: These provide protection against residual lightning energy and switching surges, installed downstream from Type 1 SPDs.
Type 3 SPDs: These offer point-of-use protection for sensitive equipment.
Including SPDs in the combiner box is essential for safeguarding the solar array from potentially destructive voltage surges.
3. Busbars
Busbars are conductive bars within the combiner box that collect the electrical output from multiple strings and distribute it evenly to the output cables. They are made from materials with excellent electrical conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, to minimize power loss.
Positive Busbar: Aggregates the positive outputs from all strings.
Negative Busbar: Aggregates the negative outputs from all strings.
Busbars ensure that the electrical load is balanced, reducing resistance and power loss, which enhances the overall efficiency of the PV system.
5. Monitoring Equipment (Optional)
Some advanced PV combiner boxes include monitoring equipment that allows users to track the performance of individual strings and the overall system. Monitoring equipment can include:
Current Sensors: Measure the current flowing through each string.
Voltage Sensors: Measure the voltage at various points in the system.
Data Loggers: Record performance data over time.
Communication Modules: Transmit data to a remote monitoring system.
Including monitoring equipment in the combiner box is particularly useful for large-scale installations, where maintaining optimal performance and quickly identifying issues are crucial.
6. Disconnect Switches
Disconnect switches are manual switches that allow the user to safely disconnect the PV system from the combiner box. They are essential for maintenance and emergency situations, providing a means to isolate the system and ensure the safety of personnel.
Load Break Switches: Designed to disconnect the system under load conditions.
Non-Load Break Switches: Used to disconnect the system when there is no current flowing.
Disconnect switches provide an additional layer of safety, allowing for easy and secure shutdown of the system when needed.
7. Enclosure
The enclosure of the PV combiner box protects the internal components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and mechanical damage. The enclosure is typically made from durable materials like metal or high-grade plastic and is designed to meet specific ingress protection (IP) ratings.
NEMA Ratings: Indicates the level of protection against dust, water, and other hazards (e.g., NEMA 3R, NEMA 4X).
IP Ratings: Specifies the degree of protection against solid objects and liquids (e.g., IP65, IP67).
A well-designed enclosure ensures the longevity and reliability of the combiner box, even in harsh outdoor conditions.
Choosing the Right PV Combiner Box
System Size and Complexity
Number of Strings: The number of solar panel strings in your system determines the number of inputs required in the combiner box. Larger systems with more strings will need a combiner box with more input terminals.
System Voltage: Ensure the combiner box is rated for the voltage of your PV system. Common system voltages include 600V, 1000V, and 1500V.
Current Rating: The combiner box should be able to handle the maximum current generated by your solar panel strings.
Type of Installation
Residential
Commercial and Industrial
Utility-Scale
Environmental Conditions
Indoor vs. Outdoor: Determine whether the combiner box will be installed indoors or outdoors. Outdoor installations require weatherproof enclosures with high ingress protection (IP) ratings.
Temperature Extremes: Consider the operating temperature range of the combiner box. For installations in areas with extreme temperatures, ensure the box is rated accordingly and includes temperature management features if necessary.
Environmental Hazards: In regions prone to lightning strikes or heavy rainfall, ensure the combiner box has adequate surge protection and is built to withstand such conditions.
Compliance and Certifications
Industry Standards: Ensure the combiner box complies with relevant industry standards, such as UL 1741 or IEC 61439. Compliance with these standards indicates that the combiner box meets safety and performance criteria.
Certifications: Look for certifications from recognized testing bodies. Certifications provide assurance that the combiner box has been rigorously tested and approved for use in PV systems.


Conclusion
PV combiner boxes are indispensable components of solar power systems, playing a crucial role in combining the electrical outputs of multiple solar panel strings into a single, streamlined output. Their importance in ensuring the efficiency, safety, and reliability of photovoltaic systems cannot be overstated. Whether for residential, commercial, or utility-scale installations, the right PV combiner box can significantly impact the overall performance and longevity of a solar power setup.
Choosing the appropriate PV combiner box requires a comprehensive understanding of several key factors. These include the size and complexity of the solar power system, the environmental conditions where the combiner box will be installed, and the specific protection and monitoring features needed. By considering these factors, you can ensure that your PV combiner box not only meets the current needs of your system but also accommodates potential future expansions.
FAQ`s.
What is the lifespan of a PV combiner box?
The lifespan of a PV combiner box typically ranges from 10 to 25 years, depending on the quality of the components and the environmental conditions in which it is installed. Regular maintenance can help extend its longevity.
Can I install a PV combiner box myself?
While it is possible for individuals with electrical experience to install a PV combiner box, it is recommended to have a professional installer handle the installation. This ensures compliance with safety standards and optimal system performance.
How do I know if my PV combiner box is faulty?
Signs of a faulty PV combiner box include no power output, intermittent power supply, frequent tripping of circuit breakers, and visible damage to the box or its components. Regular monitoring and maintenance can help detect issues early.
Are smart PV combiner boxes worth the investment?
Smart PV combiner boxes are worth the investment for larger and more complex solar installations. They offer advanced monitoring and diagnostic capabilities that enhance system performance and facilitate maintenance, potentially saving costs in the long run.
What maintenance does a PV combiner box require?
Regular maintenance of a PV combiner box includes inspecting for loose connections, checking the condition of fuses and circuit breakers, cleaning any dust or debris, and ensuring that surge protection devices are functioning correctly. Periodic professional inspections are also recommended to maintain optimal performance.
Suki Shi
My name is Suki Shi, the Sales Manager of MOREDAY. With five years of experience in this industry, I bring a wealth of industry knowledge and expertise. My goal is to support our customers in finding the best solutions for their new energy needs and to promote the adoption of sustainable power sources worldwide.













