Introduction
I
n the world of electrical systems, ensuring safety and efficiency is paramount. Among the numerous components that contribute to these goals, the isolator switch stands out as a critical device. Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, isolator switches play a vital role in managing and maintaining electrical circuits.
But what exactly is an isolator switch? At its core, an isolator switch is a manually operated mechanical switch that disconnects a part of an electrical circuit. This disconnection ensures that a particular section of the circuit is de-energized, allowing for safe maintenance and repairs. The significance of isolator switches goes beyond mere functionality; they are integral to the safety protocols of electrical systems.
Understanding the nuances of isolator switches, from their types and components to their applications and benefits, is essential for anyone involved in the design, installation, or maintenance of electrical systems. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of isolator switches, shedding light on their importance and practical applications.
Understanding Isolator Switches
An isolator switch, also known as a disconnector, is a device used to ensure that an electrical circuit is completely de-energized for maintenance or service. Unlike circuit breakers, which can automatically interrupt the flow of current in case of an overload or short circuit, isolator switches are manually operated. This means that they require human intervention to either open or close the circuit.
The primary purpose of an isolator switch is to provide a safe environment for maintenance work by isolating a section of the electrical system. When the switch is in the open position, it breaks the electrical connection, ensuring that the section of the circuit is completely de-energized. This manual operation ensures that there is no risk of accidental re-energization during maintenance activities, protecting both personnel and equipment.
Types of Isolator Switches
Isolator switches come in various types, each designed for specific applications and operating conditions. Understanding the different types can help in selecting the right isolator switch for a given application.
Single-Break Isolator Switch
A single-break isolator switch features a single point where the circuit is interrupted. This type is typically used in lower voltage applications where the electrical load is not too high. The single-break design provides a straightforward and reliable means of isolating electrical circuits. These switches are often used in residential and small commercial applications where simplicity and reliability are essential.
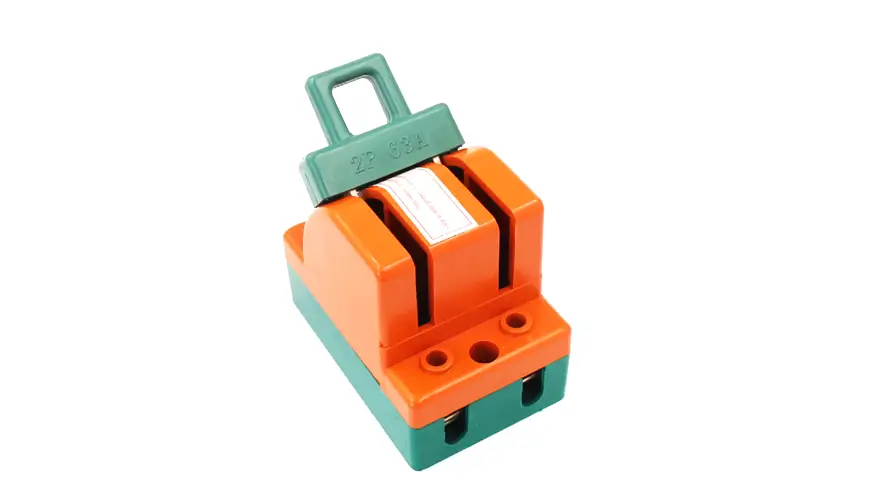

Key Features:
Single Point Interruption: Only one contact point is broken to isolate the circuit.
Lower Voltage Applications: Ideal for environments with lower electrical loads.
Simple Design: Easy to operate and maintain.
Common Uses:
Residential Electrical Panels: To isolate individual circuits for maintenance.
Small Commercial Buildings: For isolating specific sections of the electrical system.
Double-Break Isolator Switch
The double-break isolator switch has two points of interruption, providing a higher level of safety and reliability. This type is often used in higher voltage applications, where additional protection is necessary to ensure complete isolation. The double-break design ensures that even if one contact fails, the second will maintain isolation, offering an added layer of safety.
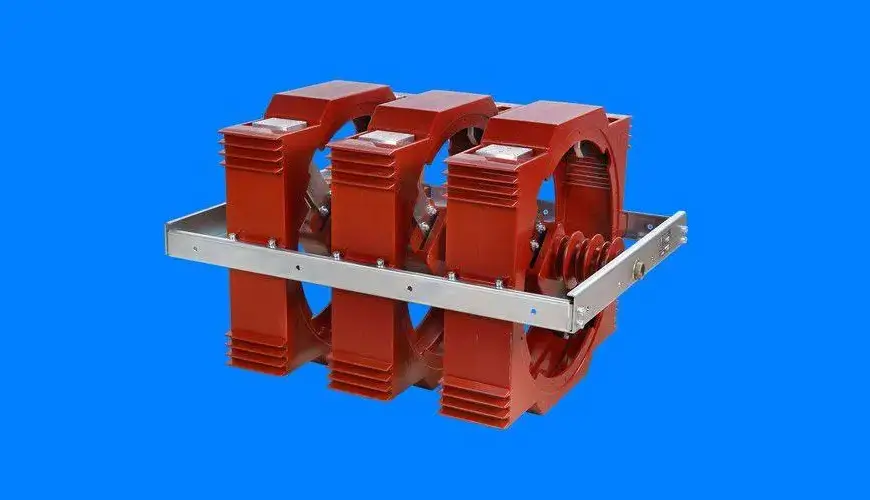

Key Features:
Dual Point Interruption: Two contact points provide enhanced isolation.
Higher Voltage Applications: Suitable for environments with higher electrical loads.
Increased Safety: Reduces the risk of accidental re-energization.
Common Uses:
Commercial Buildings: For isolating larger sections of the electrical system.
Industrial Facilities: Where higher voltage systems require robust isolation.
Pantograph Isolator Switch
Pantograph isolator switches are used in high voltage transmission systems. They have a unique design that allows them to handle high voltages and currents efficiently. The pantograph mechanism ensures a stable and reliable operation, making them suitable for demanding electrical environments. These switches are often seen in substations and power transmission networks.
Key Features:
High Voltage Handling: Designed for use in high voltage transmission systems.
Stable Operation: The pantograph mechanism provides reliable performance.
Durability: Built to withstand harsh electrical environments.
Common Uses:
Substations: For isolating sections of the power grid.
High Voltage Transmission Lines: Ensuring safe maintenance of transmission networks.
Components of an Isolator Switch
To understand how isolator switches work, it’s essential to know their main components. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the isolator switch functions correctly and safely. Here, we break down the primary components of an isolator switch:

Main Contacts
The main contacts are the heart of the isolator switch. They are responsible for making and breaking the electrical connection. When the switch is in the closed position, the main contacts are engaged, allowing electricity to flow through the circuit. When the switch is opened, the contacts separate, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity.
Key Features:
Load Handling: Main contacts are designed to handle the electrical load of the circuit.
Durability: They must withstand electrical arcing and mechanical wear over time.
Material: Typically made of conductive materials like copper or silver alloys to ensure good conductivity and longevity.
Importance:
Reliable Operation: The quality of the main contacts directly impacts the reliability and safety of the isolator switch.
Arc Management: Effective design helps in managing electrical arcs during operation, preventing damage and ensuring longevity.
Operating Mechanism
The operating mechanism is the component that allows the isolator switch to be manually operated. It usually includes a handle or lever connected to a mechanical linkage system that moves the main contacts into the open or closed position.
Key Features:
Manual Operation: The mechanism is designed for easy manual operation, providing a clear on/off state.
Robustness: Built to withstand repeated use without failure.
Precision: Ensures that the main contacts are properly aligned when the switch is closed.
Importance:
User Safety: A well-designed operating mechanism prevents accidental operation and ensures safe handling.
Ease of Use: Ensures that the switch can be operated smoothly and reliably, even under adverse conditions.
Support Insulators
Support insulators are critical for providing the necessary insulation between the live electrical parts and the grounded parts of the switch. They ensure that electrical current does not unintentionally flow to other parts of the switch or to the ground, which could cause short circuits or other electrical faults.
Key Features:
Insulation Material: Made from high-quality insulating materials like porcelain, glass, or polymer composites.
Mechanical Strength: Must support the weight and mechanical stresses of the switch components.
Dielectric Strength: Capable of withstanding high voltage without breaking down.
Importance:
Electrical Safety: Prevents accidental electrical paths that could lead to shocks or short circuits.
Reliability: Ensures the isolator switch operates safely and efficiently over its lifespan.
Additional Components
Besides the primary components, isolator switches may include additional parts depending on their design and application. These can include:
Arc Chutes:
Function: Helps to extinguish electrical arcs when the contacts open.
Material: Made from heat-resistant materials to manage high temperatures.
Interlocks:
Function: Prevents the switch from being operated under unsafe conditions.
Types: Mechanical or electrical interlocks that ensure safe operation.
Indicator Lights:
Function: Provides visual confirmation of the switch’s status (on/off).
Usage: Enhances safety by providing clear indications to the operator.
Working Principle of Isolator Switches
The working principle of isolator switches revolves around their primary function: to safely disconnect and isolate a portion of the electrical circuit. Here’s a detailed look at how isolator switches operate:
Manual Operation
Isolator switches are manually operated, meaning they require physical intervention to open or close the circuit. This manual operation is a key feature that distinguishes isolator switches from circuit breakers, which can automatically interrupt the current flow.
Opening the Switch: When the switch is in the open position, the main contacts are separated, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. This ensures that the isolated section of the circuit is completely de-energized, making it safe for maintenance or repairs.
Closing the Switch: When the switch is in the closed position, the main contacts are engaged, allowing electricity to flow through the circuit. This restores power to the isolated section, enabling normal operation.
Ensuring Safety
The primary purpose of an isolator switch is to provide a safe environment for maintenance and repairs. By physically separating the contacts, the switch ensures that there is no accidental flow of electricity, protecting both personnel and equipment.
Locking Mechanisms: Many isolator switches come with locking mechanisms that allow the switch to be locked in the open position. This prevents accidental closure and ensures the safety of maintenance personnel.
Visual Indicators: Some isolator switches include visual indicators that show the status of the switch (open or closed). This provides an additional layer of safety by clearly indicating whether the circuit is energized or de-energized.
Isolation Process
The isolation process involves several steps to ensure that the circuit is safely de-energized:
Identify the Section to be Isolated: Determine the specific section of the electrical system that requires isolation for maintenance or repairs.
Open the Isolator Switch: Manually operate the switch to open the main contacts and break the circuit. Ensure that the switch is securely locked in the open position if applicable.
Verify De-Energization: Use appropriate testing equipment to verify that the isolated section is completely de-energized. This step is crucial to ensure the safety of maintenance personnel.
Perform Maintenance or Repairs: Once the isolated section is confirmed to be de-energized, maintenance or repairs can be safely performed.
Close the Isolator Switch: After completing the maintenance or repairs, manually operate the switch to close the main contacts and restore power to the isolated section.
Benefits of Using Isolator Switches
Isolator switches offer a range of benefits that make them indispensable in various electrical systems. Here, we delve deeper into the key advantages of using isolator switches:
Safety
The primary benefit of isolator switches is safety. Electrical systems can be hazardous, and the ability to de-energize a section of the circuit is crucial for protecting maintenance personnel and preventing accidents.
Protection Against Electrical Shocks: By ensuring that a section of the circuit is completely de-energized, isolator switches protect maintenance workers from the risk of electrical shocks. This is especially important in high-voltage environments where even minor mistakes can be fatal.
Prevention of Accidental Re-Energization: Isolator switches can be locked in the open position, preventing accidental closure and ensuring that maintenance work is carried out safely. This locking mechanism is vital in industrial settings where multiple personnel may be working on different parts of the system.
Clear Visual Indication: Many isolator switches come with visual indicators that show whether the switch is open or closed. This clear indication helps prevent mistakes and ensures that everyone involved in the maintenance process is aware of the switch’s status.

Maintenance
Isolator switches make it easier to perform maintenance tasks on electrical systems. They allow specific parts of the system to be serviced without shutting down the entire system.
Localized Isolation: With isolator switches, you can isolate a specific section of the electrical circuit. This means that maintenance work can be performed on one part of the system while the rest remains operational. This localized isolation is particularly beneficial in industrial settings where shutting down the entire system can be costly and disruptive.
Ease of Access: Isolator switches are typically installed in easily accessible locations, making it simple for maintenance personnel to disconnect and reconnect the circuit as needed. This ease of access reduces downtime and improves overall maintenance efficiency.
Improved Maintenance Scheduling: The ability to isolate sections of the circuit allows for more flexible and efficient maintenance scheduling. Maintenance can be performed during off-peak hours or in a staggered manner, minimizing disruption to normal operations.
Isolator Switches in Solar Energy Systems
Isolator switches play a vital role in solar energy systems. They provide a means to disconnect solar panels from the rest of the system for safe maintenance and repairs.
Role in Solar Panel Installations
Isolator switches are installed between the solar panels and the inverter. They allow the panels to be safely isolated for maintenance or in case of emergencies.
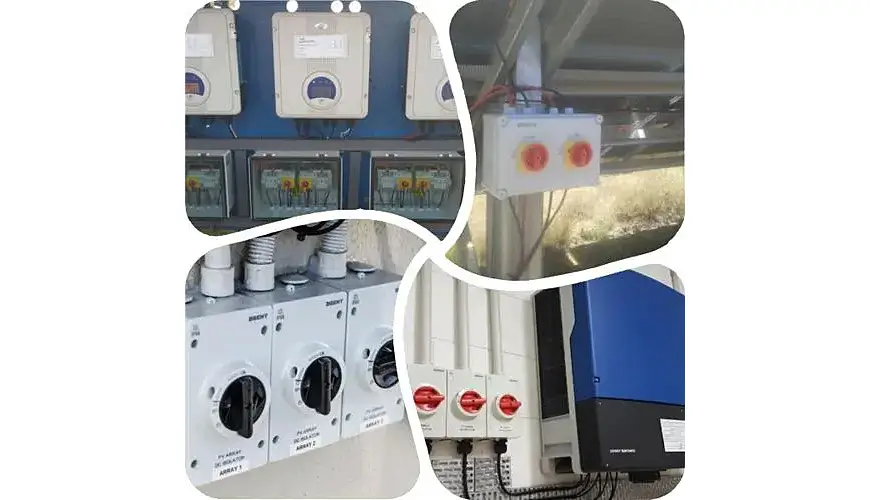

Advantages in Renewable Energy Systems
Isolator switches enhance the safety and reliability of renewable energy systems. They ensure that maintenance can be performed without risking the safety of personnel or damaging the equipment.
Isolator Switches vs. Circuit Breakers
While isolator switches and circuit breakers are both crucial components of electrical systems, they serve different purposes.
Key Differences
Operation: Isolator switches are manually operated, while circuit breakers can operate automatically.
Function: Circuit breakers protect against faults and overloads, whereas isolator switches are used for isolation during maintenance.
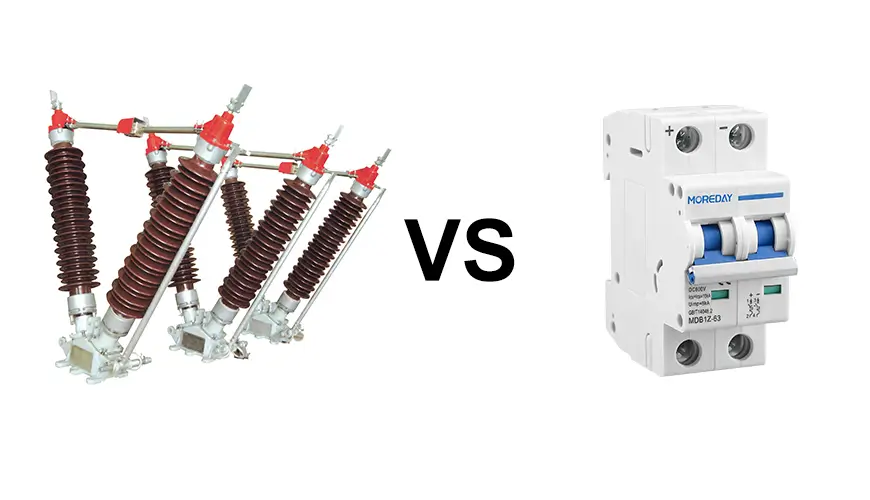
When to Use Each Device
Use isolator switches when you need to safely isolate a section of the circuit for maintenance. Use circuit breakers to protect the system from faults and overloads.
Conclusion
Isolator switches are indispensable components in electrical systems, providing safety, maintenance ease, and operational flexibility. By understanding their types, components, and benefits, you can make informed decisions about their use in various applications, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of your electrical circuits.
FAQ`s.
What is the difference between an isolator switch and a circuit breaker?
Isolator switches are manually operated devices used to de-energize a section of the circuit for maintenance. Circuit breakers, on the other hand, automatically interrupt the current flow in case of faults such as overloads or short circuits.
How often should an isolator switch be maintained?
Isolator switches should be inspected and maintained regularly, typically every six months to a year, depending on the application and environmental conditions.
Can I install an isolator switch myself?
While it is possible to install an isolator switch yourself, it is recommended to hire a professional electrician to ensure proper installation and compliance with safety standards.
Are isolator switches necessary for solar panel systems?
Yes, isolator switches are essential for solar panel systems as they allow for the safe isolation of the panels from the rest of the system for maintenance or emergencies.
What are the signs of a faulty isolator switch?
Signs of a faulty isolator switch include difficulty in operating the switch, visible wear or corrosion, unusual noises during operation, and failure to properly isolate the circuit.
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.