In today’s rapidly evolving energy landscape, more systems rely on direct current (DC) to power devices, from electric vehicles to renewable energy installations. This shift makes DC circuit breakers indispensable in ensuring these systems remain safe and functional. But what exactly is a DC circuit breaker, and why is it so important? In this article, we’ll dive deep into everything you need to know about DC circuit breakers—from how they work to their real-world applications and more.
What is a DC Circuit Breaker?
At its core, a DC circuit breaker is a protective device designed to interrupt the flow of direct current in a circuit when it exceeds a certain threshold. Think of it as a safety net that steps in when the current running through your system gets out of control. Without it, the excess current could cause overheating, damage to devices, or even fires.
Unlike AC (alternating current) circuit breakers, which are used for power that alternates direction, DC circuit breakers deal with the continuous, one-directional flow of direct current. This small difference in the nature of the current requires DC circuit breakers to be specifically designed to handle the unique challenges of DC systems.
In short: DC circuit breakers keep your system safe from electrical hazards, and they are absolutely essential in DC power systems like solar installations or battery energy storage setups.
How DC Circuit Breakers Work
So, how does a DC circuit breaker actually operate? While the technical aspects can get complex, the basic working principle is pretty straightforward. The breaker constantly monitors the current flowing through the circuit. If it detects an abnormality—such as an overload, short circuit, or fault—it acts by opening the circuit, cutting off the electricity, and preventing further damage.
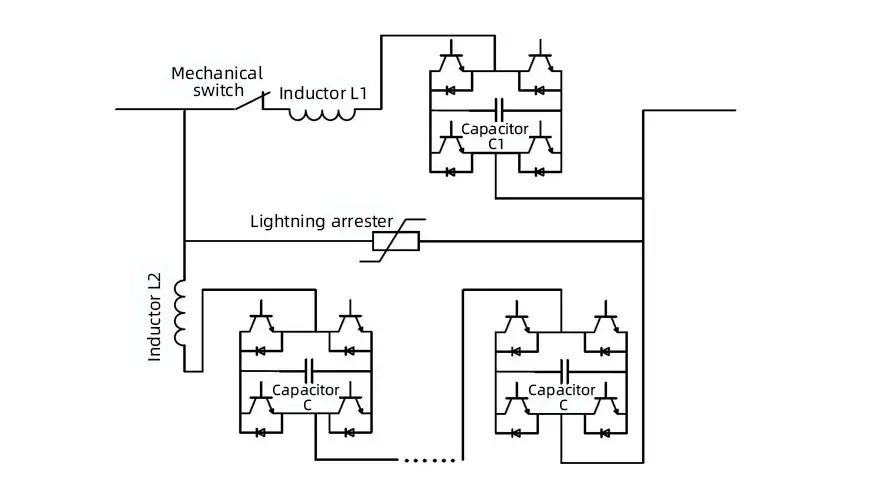
Here’s a simplified version of how it works:
- Current Sensing: The breaker uses sensors to keep tabs on the current in the circuit.
- Trip Unit: When the current goes beyond a safe level, the trip unit sends a signal to activate the breaker.
- Arc Suppression: As the breaker opens, an electrical arc forms, which is dangerous if not handled properly. DC circuit breakers use special arc suppression mechanisms to extinguish the arc quickly.
- Power Interruption: Once the arc is gone, the circuit is fully interrupted, isolating the faulty section and protecting the rest of the system.
- Reset: After the fault is cleared, the breaker can be manually or automatically reset, allowing normal operation to resume.
The complexity of a DC circuit breaker lies in how it handles arcs. Since DC doesn’t alternate like AC, the breaker doesn’t have the benefit of zero-crossing points (which naturally occur in AC systems and make arc extinction easier). That’s why DC circuit breakers rely on advanced techniques like magnetic arc suppression or exhaust chambers to safely break the current.
Types of DC Circuit Breakers
Not all DC circuit breakers are the same. Depending on your application, you might need a different type of breaker to protect your system. Here’s a quick breakdown of the most common types:
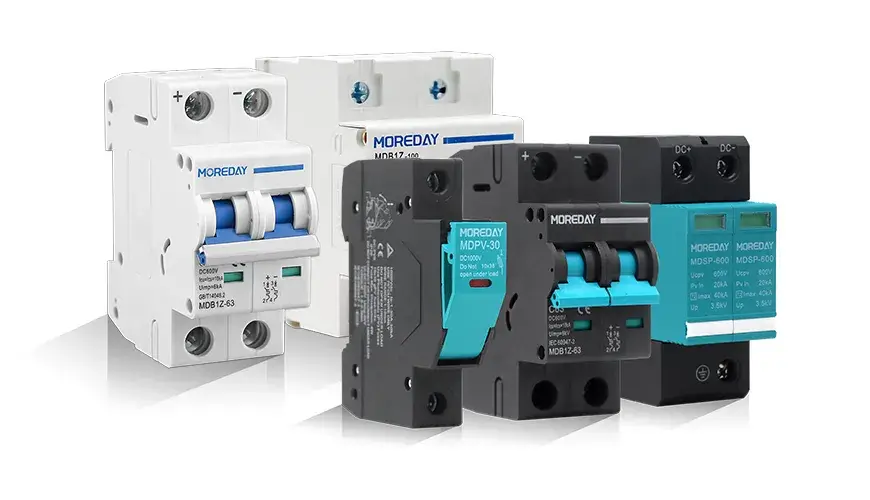
1. DC Miniature Circuit Breaker (DC MCB)
The DC MCB is designed for lower-voltage DC systems and is commonly used in applications like solar panels or battery storage systems. It’s perfect for residential setups or small-scale industrial uses. Despite its small size, the MCB provides reliable protection against short circuits and overloads.
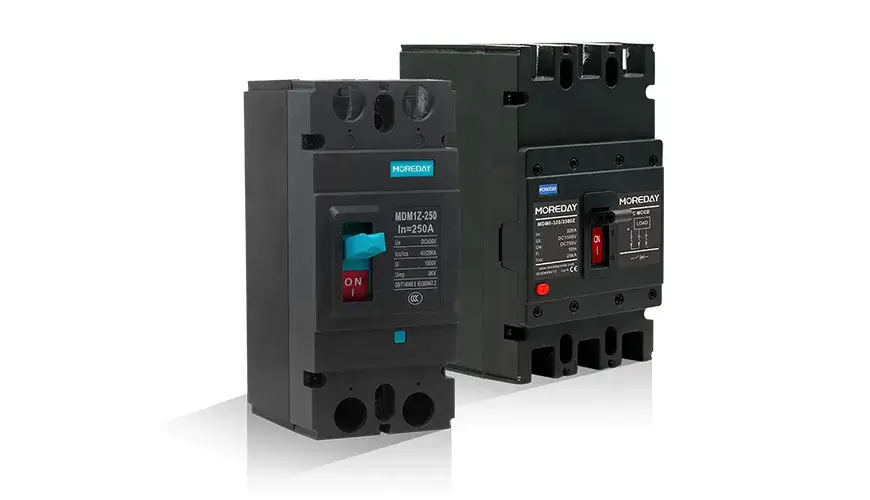
2. DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker (DC MCCB)
If you’re dealing with higher voltages and larger currents, the DC MCCB is your go-to breaker. This type is ideal for heavy-duty tasks in commercial and industrial settings, offering thermal overload protection, short circuit protection, and adjustable trip settings. You’ll often see MCCBs in larger energy storage systems and transport applications.
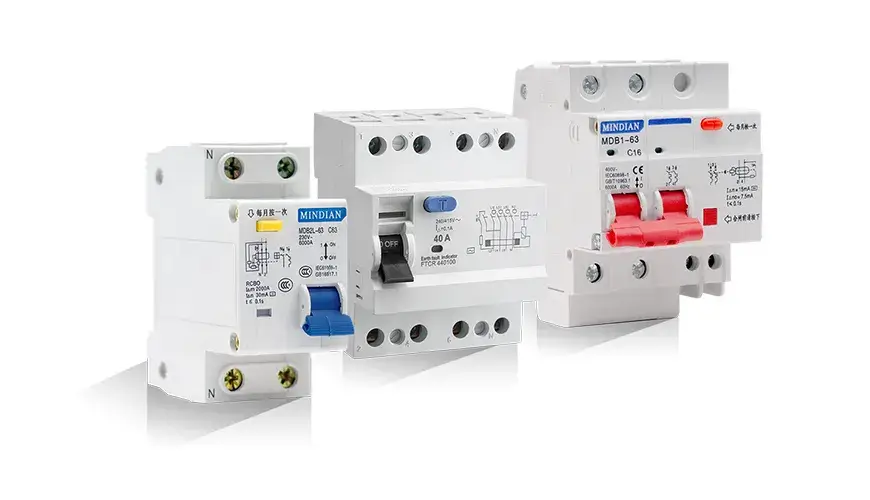
3. Type B Residual Current Device (RCD)
The Type B RCD is more specialized and focuses on detecting residual currents (often caused by faults or leaks) and shutting down the system before they become a safety hazard. This device is commonly used in homes and industrial systems where there’s a higher risk of electrical faults.
By choosing the right type of DC circuit breaker for your system, you can ensure that it’s both safe and efficient. This decision depends largely on your system’s voltage and current requirements.
Key Applications of DC Circuit Breakers
So, where exactly do you find DC circuit breakers in action? As our world moves toward renewable energy, DC circuit breakers are becoming more and more common. Here are some of the key areas where they play a vital role:
1. Solar Photovoltaic Systems
Solar power systems rely heavily on DC circuit breakers to protect solar panels, inverters, and batteries. Since solar panels generate direct current, these breakers are crucial in ensuring the safety of both the system and the people operating it. Without DC breakers, a fault in the system could lead to equipment damage or even pose fire hazards.
2. Battery Energy Storage Systems
With the rise of renewable energy, battery energy storage systems (BESS) are growing in popularity. Whether it’s a small residential system or a large grid-scale setup, DC circuit breakers are essential in protecting the batteries and associated equipment. They help regulate the current flow and prevent overloading during charging and discharging cycles.
3. Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
As the electric vehicle (EV) market expands, so too does the need for DC circuit breakers in EV charging infrastructure. Charging stations, especially those for fast charging, operate on direct current, making DC circuit breakers indispensable for safe and efficient operation.
4. Industrial Applications
Many industrial processes rely on DC power for machines, tools, and automation systems. In these cases, DC circuit breakers provide critical protection from electrical faults, ensuring the safety of both the equipment and the personnel operating it.
The Importance of DC Circuit Breakers in Renewable Energy
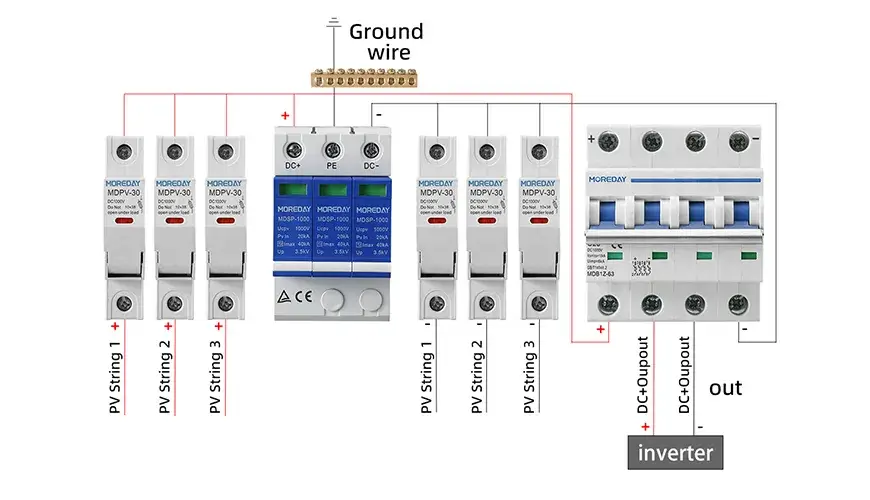
As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy, the role of DC circuit breakers becomes even more critical. Solar power systems, for instance, generate direct current, which needs to be managed safely to prevent damage to the system or potential fire hazards. DC circuit breakers are the backbone of these systems, ensuring they run smoothly and safely.
Moreover, as energy storage becomes a major component of renewable energy systems, battery storage solutions depend heavily on the protection provided by DC breakers. Without them, the batteries—which store large amounts of energy—could become dangerous if overloaded or shorted. In essence, DC circuit breakers allow us to harness the power of the sun and wind safely, protecting both the infrastructure and the people using it.
How to Choose the Right DC Circuit Breaker
Choosing the correct DC circuit breaker can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be. Here are the key factors to consider when selecting one:
1. System Voltage
First, determine the operating voltage of your DC system. DC circuit breakers are rated for specific voltages, so make sure you choose one that matches or exceeds the system voltage.
2. Current Rating
You need to know the full-load current of your system. Add up the total current draw of all devices connected to the circuit and select a breaker with a current rating that’s 125% to 150% of the full-load current. This safety margin helps avoid nuisance tripping.
3. Interrupting Capacity
Ensure the circuit breaker can safely interrupt the maximum fault current that could occur in your system. This is especially important in systems like solar farms or industrial applications, where the fault current can be significantly higher than in residential setups.
4. Environmental Considerations
Consider the operating environment. For instance, if the breaker will be installed outdoors or in a harsh environment, you’ll need a breaker with a high-enclosure rating (e.g., NEMA or IP). Also, check the temperature tolerance of the breaker, as high ambient temperatures can affect performance.
5. Additional Features
Some DC breakers come with advanced features like remote trip or monitoring capabilities. Depending on your system’s needs, you may want to opt for a breaker that integrates with your monitoring systems for added convenience and safety.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select a DC circuit breaker that fits your system perfectly, ensuring reliable protection and minimal downtime.
Advantages of Using DC Circuit Breakers
So why choose a DC circuit breaker over an AC one? Here are some of the key advantages:

- Faster Response Time: DC circuit breakers react more quickly to faults because DC systems have no zero-crossing points, which means faults are detected and cleared faster than in AC systems.
- Improved Arc Extinguishing: The arc suppression mechanisms in DC breakers are more advanced, making them more effective at extinguishing arcs and preventing them from reigniting.
- Lower Voltage Drop: DC breakers typically experience less voltage loss across the contacts, which means your system runs more efficiently.
- Compact Size: For the same rated current, DC circuit breakers tend to be more compact than their AC counterparts, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium.
- Increased Selectivity: DC breakers are better at isolating only the faulty section of the circuit, reducing downtime and minimizing the impact on the rest of the system.
Safety, Maintenance, and Best Practices
While DC circuit breakers are designed to provide safety and protection, they still require routine maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Regular Inspections: Check your circuit breakers periodically to ensure they’re operating correctly. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Test the Breakers: If possible, perform periodic testing to verify that the breakers trip when they’re supposed to.
- Clean the Contacts: Dust and dirt can build up on the contacts, reducing the efficiency of the breaker. Cleaning these contacts helps maintain proper performance.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines: Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for installation, maintenance, and replacement schedules to ensure the long-term reliability of your DC circuit breakers.
Conclusion
DC circuit breakers are more than just a safety measure—they’re an essential component in modern electrical systems, especially in renewable energy and electric vehicle infrastructure. Whether you’re working with a solar farm, an energy storage system, or an EV charging station, choosing the right DC circuit breaker is crucial for ensuring your system runs efficiently and safely.
By understanding how these devices work, their types, applications, and how to choose the right one, you’ll be better equipped to protect your investments and ensure the long-term success of your electrical systems.
Related reading: Can DC MCB Use for AC?
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a DC circuit breaker and an AC circuit breaker?
The main difference lies in the type of current they control. DC circuit breakers handle direct current, which flows in one direction, while AC circuit breakers are designed for alternating current, which periodically reverses direction. This difference requires DC breakers to use more sophisticated arc-extinguishing techniques.
2. Can I use an AC circuit breaker in a DC system?
No, using an AC circuit breaker in a DC system is not recommended. DC currents don’t have natural zero-crossing points, which makes it harder for AC breakers to extinguish arcs effectively. This could result in safety hazards and system failures.
3. What are the key advantages of using DC circuit breakers in renewable energy systems?
DC circuit breakers offer faster response times, better arc extinguishing, lower voltage drops, and increased selectivity. These advantages make them ideal for protecting solar photovoltaic systems, battery storage, and other renewable energy applications.
4. How often should DC circuit breakers be maintained?
DC circuit breakers should be inspected and maintained regularly, with a recommended check every 6-12 months depending on the operating conditions. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for best practices.
5. What is the typical lifespan of a DC circuit breaker?
The lifespan of a DC circuit breaker can vary depending on usage, maintenance, and environmental conditions. However, with proper care, they can last between 10-20 years. Regular maintenance will help extend their operational life.










