Introduction
E
lectric vehicles (EVs) are not just a trend; they’re revolutionizing the way we think about transportation. At the heart of this transformation lies a crucial component: the EV power converter. Think of power converters as the “traffic cops” of an electric vehicle’s electrical system, directing and managing the flow of electrical power to ensure everything runs smoothly. In this article, we’ll explore what makes EV power converters tick, dive into cutting-edge technologies, tackle current challenges, and look at what the future holds. Buckle up—let’s drive through the world of EV power converters!
Understanding EV Power Converters
Let’s start with the basics. An EV power converter is a device that converts electrical power from one form to another to meet the needs of various components within an electric vehicle. Imagine it as a translator in a multilingual meeting, converting one language into another so everyone can understand. In an EV, this means converting high-voltage DC from the battery to the AC needed to drive the motor, or adjusting the voltage levels to power auxiliary systems.

Classification: Power converters can be divided into direct current/direct current (DC/DC) conversion, direct current/alternating current (DC/AC) conversion and alternating current/direct current (AC/DC) conversion. The DC/DC converter is mainly used in pure electric vehicles. It is an important electrical equipment to realize the conversion, transmission and electric traction of electrical system energy.
Function: A DC/DC converter is a device that converts electrical energy of one voltage value into electrical energy of another voltage value in a DC circuit. It is divided into step-down DC/DC converter, step-up DC/DC converter and bidirectional DC/DC converter. Its main functions are: driving DC motors, supplying power to low-voltage equipment, charging low-voltage batteries, and matching the characteristics of different power sources.
Driving DC motors: In steering, braking and other auxiliary systems driven by small-power DC motors, DC/DC power converters are generally used directly for power supply.
Supply power to low-voltage devices: Supply power to various low-voltage devices in electric vehicles such as lights.
Charging low-voltage batteries: In electric vehicles, a high-voltage power supply is required to charge the low-voltage batteries through a step-down DC/DC converter.
Matching characteristics between different power sources: Taking fuel cell electric vehicles as an example, a hybrid power system structure of a fuel cell group and a power battery is generally used. In an energy hybrid system, a boost DC/DC converter is used; in a power hybrid system, a bidirectional DC/DC converter is used.
A DC/AC converter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current, also known as an inverter. Electric vehicles that use AC motors must use a DC/AC converter to convert the direct current from batteries or fuel cells into alternating current.
The AC/DC converter converts AC voltage into the stable DC voltage required by electronic equipment. The function of AC/DC in electric vehicles is mainly to convert the AC power generated by the AC motor into DC power and provide it to electrical equipment or energy storage devices for storage.
Working Principle of DC/DC Converter
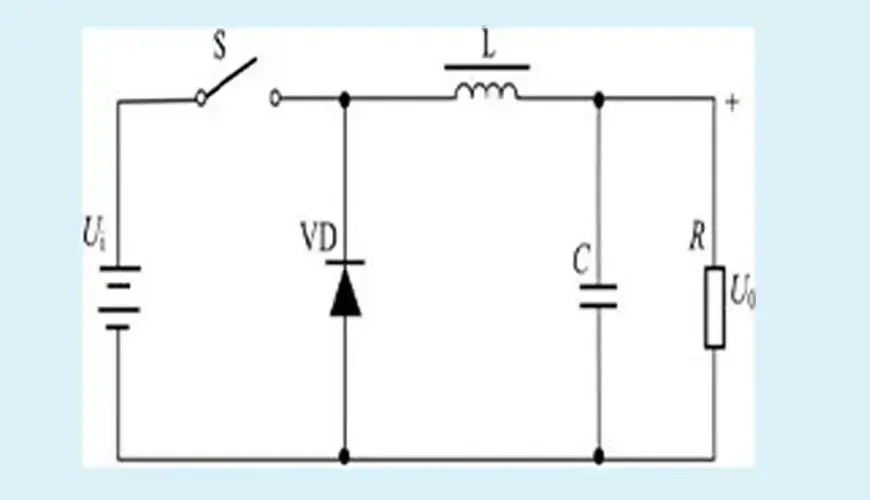
Buck DC/DC converter: When the switch S is closed, the voltage across the inductor is (Ui-U0). At this time, the inductor is excited by the voltage (Ui-U0), and the magnetic flux increased by the inductor is (Ui-U0)Ton, where Ton is the on time. When the switch is disconnected, due to the continuity of the output current, the diode VD becomes conductive, the inductor is decoupled, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductor is U0Toff, where Toff is the off time. When the state of the switch closed and the state of the switch open are balanced, (Ui-U0)Ton=(U0)Toff. Since the duty cycle is less than 1, Ui>U0, achieving the buck function.
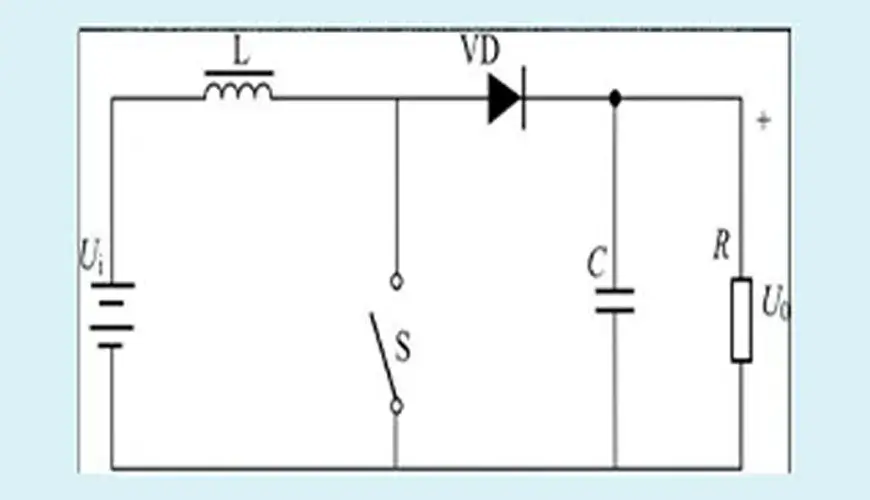
Boost DC/DC converter: When the switch S is closed, the input voltage is applied to the inductor. At this time, the inductor is excited by the voltage Ui, and the magnetic flux increased by the inductor is UiTon. When the switch is disconnected, due to the continuity of the output current, the diode VD becomes conductive, the inductor is demagnetized, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductor is (U0-Ui)Toff. When the state of the switch closed and the state of the switch open are balanced, UiTon=(U0-Ui)Toff. Since the duty cycle is less than 1, U0>Ui, and the boost function is achieved.
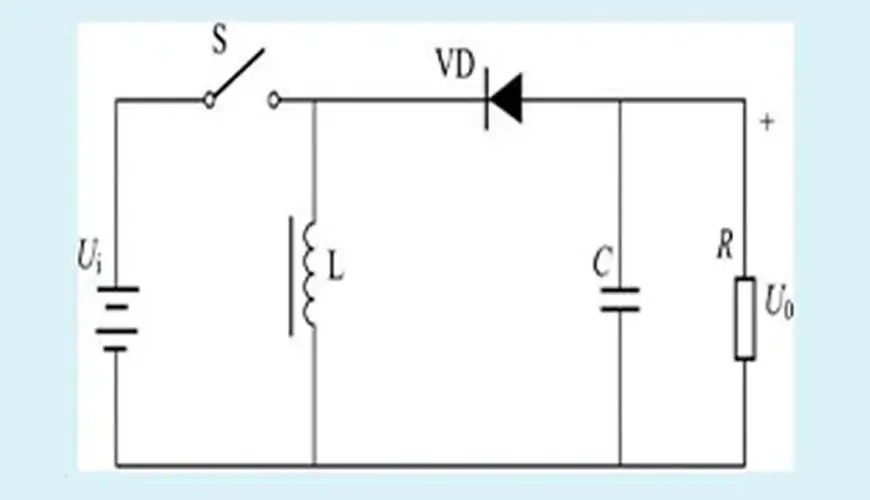
Bidirectional DC/DC converter: When the switch is closed, the inductor is excited by the voltage Ui, and the magnetic flux increased by the inductor is UiTon; when the switch is opened, the inductor is demagnetized, and the magnetic flux reduced by the inductor is U0Toff. When the state of the switch closing and the state of the switch opening reach a balance, the increased magnetic flux is equal to the reduced magnetic flux, UiTon=UOToff, depending on the values of Ton and Toff, Ui>U0 or U0>Ui may be possible.
Application of Power Converter in Electric Vehicles
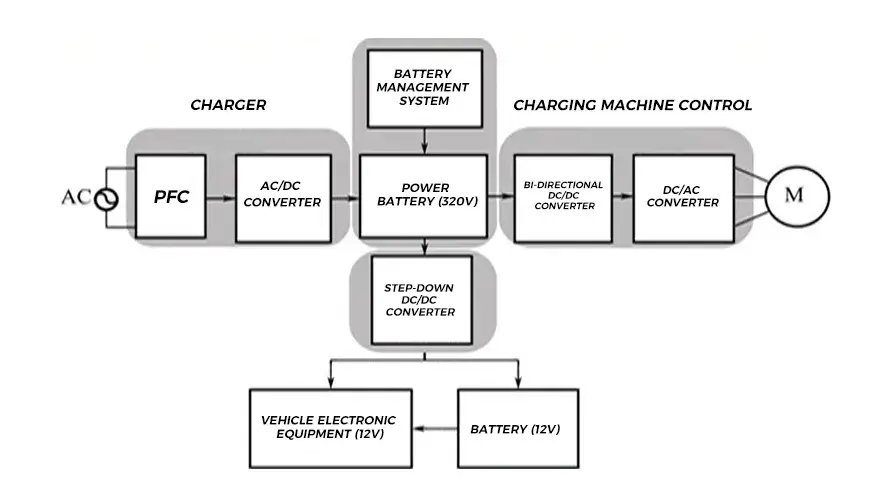
The voltage of the electric vehicle power battery is 320V, which is managed and monitored by the battery management system and charged by an on-board charger (including AC/DC converter). The AC voltage range is from 110V single-phase system to 380V three-phase system; the power battery drives the AC motor through a bidirectional DC/DC converter and DC/AC converter, and is also used for regenerative braking to store the recovered energy into the power battery; at the same time, in order to convert the 320V high voltage of the power battery into a 12V power supply that can be used by on-board electronic equipment and charge the battery, a step-down DC/DC converter is required.
Conclusion
Power converters don’t work in isolation; they interact with other systems within the EV, such as battery management and motor control. Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility is essential for optimizing overall vehicle performance. It’s like coordinating various departments in a company to ensure smooth operations and achieve common goals.
EV power converters are integral to the future of electric transportation. From understanding the basics to exploring advanced technologies, this article has highlighted the key aspects of power converters and their critical role in EVs. As technology continues to evolve, power converters will play an even more significant role in shaping the future of electric vehicles. By staying informed about the latest advancements and practical considerations, we can better appreciate the innovations driving the electric vehicle revolution.
Recommended reading: Electric Vehicle Charging Technology
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.