Introduction
I
n today’s world, where our reliance on electricity is ever-growing, ensuring electrical safety is paramount. Whether you’re setting up a residential home or managing complex industrial operations, the risk of electrical faults can’t be ignored. That’s where RCCBs (Residual Current Circuit Breakers) come into play. These clever devices can be lifesavers—literally! They protect us from electric shocks and reduce the risk of fires by quickly cutting off power when a problem arises.
But how do you choose the right RCCB for your needs? With so many options out there, it can feel like navigating a maze. Don’t worry; we’ve got you covered! In this guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about RCCBs, from how they work to the different types available. Let’s dive in and discover why choosing the right RCCB can make all the difference.
What is an RCCB and How Does It Work?
Let’s start with the basics. An RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) is a device designed to prevent electric shocks and fires caused by leakage currents. Sounds fancy, right? Essentially, it monitors the current flowing through the live and neutral wires. In an ideal situation, the current in both wires should be equal. But if there’s a fault—like someone touching a live wire or a damaged appliance causing a leak to the ground—the current gets imbalanced. The RCCB detects this imbalance and trips the circuit in milliseconds, cutting off the power.
This quick response is what makes RCCBs so vital. Whether you’re protecting your home or an industrial plant, RCCBs provide that extra layer of safety that traditional circuit breakers can’t. Think of them as the unsung heroes of your electrical system—working silently in the background to keep you safe.
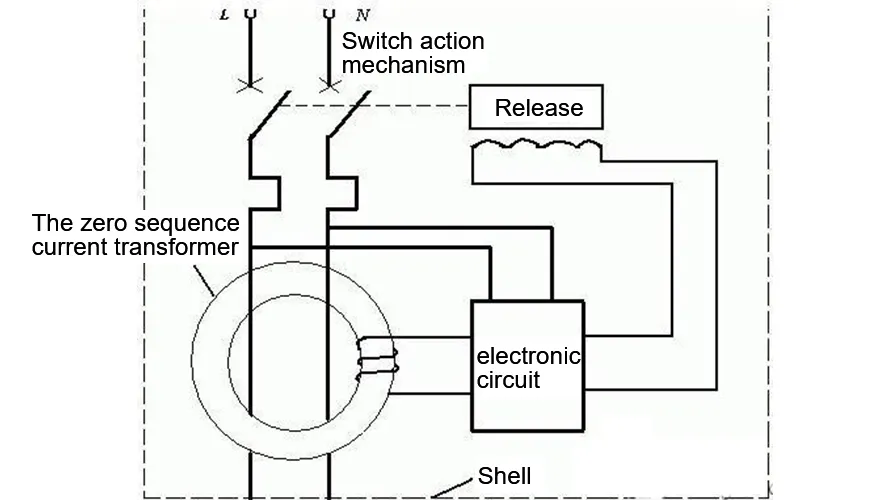

Types of RCCBs Explained: Which One Do You Need?
When it comes to choosing the right RCCB, it’s essential to understand the different types. Just like cars, RCCBs come in various models, each designed for specific situations. So, how do you know which one is right for you? Let’s break it down:
Type AC RCCB
This is your basic model and the most common type found in homes. It’s designed to detect alternating currents (AC). If you’re dealing with standard household appliances like lights and outlets, a Type AC RCCB will do the job.
Type A RCCB
Looking for something a bit more sophisticated? The Type A RCCB detects both AC and pulsating direct currents (DC). It’s perfect for homes and buildings that use electronics like washing machines, computers, or LED lights. These devices can generate DC currents that a Type AC wouldn’t catch, so if you’ve got modern tech, Type A is a must.
Type F RCCB
Now, we’re getting into the big leagues. The Type F RCCB is designed for mixed-frequency currents, which you’ll find in high-end equipment or industrial machinery, like Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). This type is ideal for more complex setups, where protecting your valuable equipment is as important as protecting people.
Type B RCCB
Finally, we’ve got the Type B RCCB—the ultimate protection device. It detects AC, pulsating DC, and pure DC currents, making it essential for setups with renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or electric vehicle (EV) chargers. Type B RCCBs are versatile and can handle the most complex current types, ensuring your green energy projects run smoothly.
Advanced Protection: Understanding RCBOs and How They Differ from RCCBs
Now, here’s where things get a little more interesting. You’ve probably heard of RCCBs, but what about RCBOs? These nifty devices combine the functions of both an RCCB and a traditional circuit breaker. While RCCBs protect against ground faults, RCBOs offer protection against overcurrent and short circuits as well.
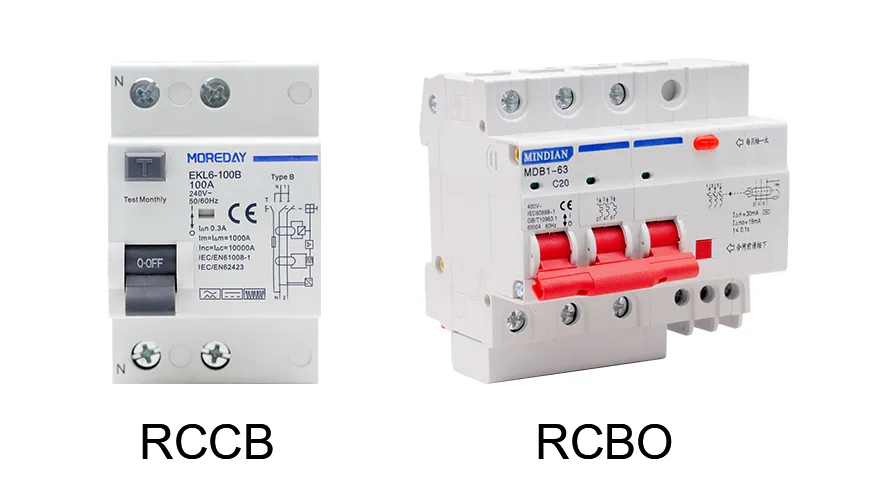


Imagine having to install separate devices to handle ground faults and overcurrent protection—what a headache! With an RCBO, you get two devices in one compact unit, saving space and making installation easier. They’re ideal for setups where comprehensive protection is needed, but space is limited, like in residential homes or smaller commercial setups.
For example, imagine running a small workshop with multiple machines. You need protection from both electrical faults and overloads. Instead of cluttering your panel with multiple breakers, installing an RCBO gives you the best of both worlds.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an RCCB
Choosing the right RCCB isn’t just about picking the most expensive or advanced model. You need to consider your specific needs. Here’s what you should keep in mind:
1. Current Rating and Sensitivity
RCCBs come with different sensitivity levels, typically 30mA for human protection and 300mA for fire protection. If you’re installing an RCCB in a home, you’ll want the 30mA model to protect against electric shocks. But in industrial settings, a 300mA RCCB might be needed to prevent electrical fires.
2. Installation Environment
Where are you installing your RCCB? Is it indoors or outdoors? In a residential or industrial setup? This matters because outdoor or industrial environments might require RCCBs with higher IP ratings (protection against dust and water).
3. Compliance with Standards
Always ensure that your RCCB complies with international standards, such as IEC 61008 and IEC 61009. This guarantees the device meets the required safety and performance criteria. If you’re in a specific country with local codes, make sure your RCCB is compliant with those too.
4. Type of Load
What kind of electrical load are you dealing with? If it’s simple residential appliances, a basic RCCB might be sufficient. But if you’re protecting complex industrial machinery or renewable energy systems, you’ll need something more advanced, like a Type B RCCB.
5. Installation and Maintenance Costs
RCCBs are an investment, but they can save you from expensive damage down the line. Think about both the initial cost and the long-term savings. It’s not just about buying the cheapest model—it’s about choosing the one that will provide reliable protection for years to come.
Applications of RCCBs in Modern Electrical Systems
Let’s talk about real-world applications. RCCBs aren’t just for electrical nerds—they’re used in a wide range of environments, from homes to factories to renewable energy systems.
1. Smart Homes
With the rise of smart home technology, more devices are connected to our electrical systems than ever before. RCCBs are crucial in protecting all those gadgets from ground faults. Imagine your smart thermostat, security cameras, and lights all going down because of a small electrical fault. An RCCB ensures that doesn’t happen.
2. Industrial Automation
In industrial environments, RCCBs play a critical role in preventing equipment failures. Machines are expensive, and downtime is even more costly. A well-placed RCCB can detect faults and isolate them before they cause major damage, ensuring operations run smoothly.
3. Solar and Renewable Energy
Renewable energy systems, like solar panels or EV charging stations, can produce a mix of AC and DC currents. This is where Type B RCCBs shine. They can handle both types of currents, ensuring your green energy project is protected from faults. Plus, in many places, installing RCCBs is required by law for solar systems.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Getting the most out of your RCCB starts with proper installation. It’s like buying a top-of-the-line sports car—you want to make sure it’s set up correctly to get the best performance.
Installation Tips:
- Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions. RCCBs are sensitive devices, and a mistake during installation can render them ineffective.
- Make sure the RCCB is rated for the correct current and sensitivity for your setup. Don’t install a residential RCCB in an industrial plant!
- Verify wiring connections are secure, and use proper tools to avoid damaging the RCCB during installation.
- For industrial setups, ensure that the RCCB is placed in a dust- and moisture-resistant enclosure.


Maintenance Tips:
- Regularly test your RCCB using the built-in test button. This ensures it’s functioning correctly and will trip in the event of a fault.
- Schedule routine checks to inspect for wear and tear, especially in high-use environments like factories.
- If your RCCB trips frequently, don’t ignore it! This could indicate an underlying issue, like faulty wiring or a malfunctioning appliance. Get a professional to check it out.
Troubleshooting Common RCCB Issues
Even the best RCCBs can sometimes act up. Here’s how to troubleshoot common issues:
- Frequent Tripping: This might be caused by faulty appliances or wiring issues. Check for damaged equipment or exposed wires that could be causing leakage currents.
- Failure to Reset: If the RCCB won’t reset after tripping, it could be a sign of a persistent fault. Turn off all connected devices and try again. If it still won’t reset, call an electrician.
- Nuisance Tripping: Sometimes, RCCBs trip for no apparent reason. This could be due to sudden load shifts or electrical interference. Check your appliances and the RCCB’s placement.
Comparing RCCBs with Other Safety Devices: RCCBs vs. Circuit Breakers, Fuses, and ELCBs
Now, let’s pit RCCBs against their electrical cousins:


RCCBs vs. Fuses
Fuses are designed to protect against overcurrent by melting and disconnecting the circuit. But unlike RCCBs, they can’t detect ground faults. That means if there’s an electric shock risk, the fuse won’t help. RCCBs provide an extra layer of protection by addressing ground faults, which fuses can’t detect.
RCCBs vs. Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers trip when they detect too much current flowing through the circuit. However, they don’t monitor for ground faults like RCCBs. A combination of the two (known as an RCBO) offers comprehensive protection.
RCCBs vs. ELCBs
ELCBs (Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers) are older technology. They require a separate earthing connection and are less sensitive than RCCBs. Nowadays, RCCBs have largely replaced ELCBs due to their superior sensitivity and ease of use.
MOREDAY’s Commitment to Quality and Compliance
At MOREDAY, we don’t just make RCCBs—we engineer peace of mind. Our RCCBs are built to the highest standards, ensuring they meet both international and local safety regulations. Each product undergoes rigorous testing, so you can trust it to protect your electrical systems for years to come.
We know that every application is different, which is why we offer a wide range of RCCBs, from basic residential models to high-tech industrial devices. No matter what your electrical setup looks like, MOREDAY has the right RCCB for you.
Conclusion
Choosing the right RCCB isn’t just about ticking boxes—it’s about ensuring the safety of your home, workplace, or renewable energy project. With the right RCCB, you’re protecting not only your electrical systems but also the people who rely on them every day.
Whether you’re safeguarding a smart home, an industrial operation, or a solar farm, an RCCB is a small investment that makes a big difference. So don’t cut corners—choose the RCCB that fits your needs, and rest easy knowing your electrical system is in safe hands.
FAQ`s.
Q1: What’s the difference between RCCB and RCBO?
A1:An RCCB protects against ground faults, while an RCBO combines ground fault protection with overcurrent protection. An RCBO is essentially an RCCB and a circuit breaker in one device.
Q2: How often should I test my RCCB?
A2: It’s recommended to test your RCCB every 3-6 months using the built-in test button. This ensures the device is working correctly and will trip in case of a fault.
Q3: Can I install an RCCB myself?
A3: While it's possible for those with electrical experience, it's generally safer to hire a professional electrician. Incorrect installation can render the RCCB ineffective.
Q4: Are RCCBs mandatory for solar energy systems?
A4: In many regions, installing an RCCB is required by law for solar systems. They’re critical in protecting both the system and users from electrical faults, particularly in renewable energy setups.
Q5: What should I do if my RCCB keeps tripping?
A5: Frequent tripping could indicate a fault in your electrical system, such as damaged wiring or faulty appliances. It’s best to have a qualified electrician inspect the issue to ensure your system is safe.
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.