Introduction
T
he electric vehicle (EV) market is on fire, and it’s not slowing down anytime soon. With the demand for cleaner, greener transportation, EV technology is evolving at a breakneck pace. But here’s the kicker: while most of the buzz is around flashy new models and sleek designs, the real game-changer lies in something you can’t even see—the voltage running through your car’s veins. Let’s dive into the electrifying world of EV charging technology and explore how innovations beyond the 800V architecture are not just reshaping the road but redefining the future.
From 400V to 800V: What’s the Big Deal?
You’ve probably heard the chatter—800V systems are the future, right? But before we jump onto that bandwagon, let’s rewind a bit and understand why this is such a big deal.
Most EVs on the road today run on a 400V architecture. Think of it as the gold standard, a well-trodden path that automakers have followed for years. The 400V system has been reliable, cost-effective, and, let’s be honest, it’s gotten us pretty far. But, like any technology, there’s always room for improvement.
Enter the 800V system—a new kid on the block, but one that’s quickly gaining popularity. This isn’t just a minor upgrade; it’s like switching from dial-up to fiber optic internet. With 800V, everything gets faster, lighter, and more efficient. But, as with all shiny new toys, there’s more to the story.
400V vs. 800V: A Head-to-Head Comparison
So, what exactly sets these two systems apart? Let’s break it down.
400V Systems: The tried-and-true 400V architecture has been the backbone of the EV industry. It’s reliable, well-understood, and—most importantly—affordable. Because the infrastructure for 400V systems is so widespread, it’s easy to find a compatible charging station just about anywhere. However, 400V systems aren’t perfect. They’re bulkier, heavier, and—here’s the kicker—slower to charge. If you’ve ever found yourself tapping your foot impatiently while waiting for your EV to charge, you’ve probably got a 400V system to thank.
800V Systems: On the flip side, 800V systems are like the Ferrari of EV architectures—sleek, fast, and undeniably impressive. By doubling the voltage, these systems cut charging times significantly. They also allow for thinner cables and lighter components, which means less weight and more efficiency. But, of course, all that glitters isn’t gold. 800V systems are more expensive to produce, and the infrastructure to support them is still catching up. Finding an 800V charging station is like finding a needle in a haystack—possible, but not easy.
| Feature | 400V Systems | 800V Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Speed | Slower charging times due to lower voltage. | Significantly faster charging times, especially with high-powered chargers. |
| Infrastructure Compatibility | Widely compatible with existing charging stations; most public chargers support 400V. | Limited compatibility; requires 800V-specific charging stations, which are less common. |
| Cost | Lower cost due to well-established manufacturing processes and infrastructure. | Higher cost due to newer technology and less mature infrastructure. |
| Efficiency | Less efficient; higher current leads to more energy loss as heat. | More efficient; lower current reduces energy loss and heat generation. |
| Weight | Heavier components and cables due to the need to handle higher currents. | Lighter components and cables; reduced weight due to lower current requirements. |
| Market Availability | More models available; dominant in the current market. | Fewer models available; emerging technology with growing market adoption. |
| Future Proofing | Less future-proof as the industry moves towards higher-voltage systems. | More future-proof; likely to become the standard as charging infrastructure catches up. |
| Maintenance and Durability | Easier maintenance due to established technology and widespread availability of parts. | Potentially more complex maintenance due to newer, less common technology. |
| Consumer Adoption | Higher adoption due to familiarity and lower costs. | Growing adoption among premium models and tech-savvy consumers who prioritize faster charging. |
EV Models Using 400V and 800V Platforms
Now, let’s put this into perspective with some real-world examples.
400V EV Models: Many of the EVs you see zipping around town are running on 400V systems. The Nissan Leaf, Tesla Model S, and Chevrolet Bolt are all part of the 400V club. These vehicles are perfect for everyday drivers who value affordability and the ease of finding a charging station. They might not charge as quickly as their 800V counterparts, but they get the job done—and done well.
800V EV Models: If you’re looking for something with a bit more oomph, you’re in luck. The Porsche Taycan, Hyundai IONIQ 5, and Lucid Air are leading the charge (pun intended) in the 800V arena. These vehicles are designed for drivers who crave speed—both on the road and at the charging station. While they come with a higher price tag, the benefits of faster charging and improved efficiency make them a worthy investment for those who can afford it.

The Future of EV Charging: Beyond 800V
So, what’s next? If 800V is the future, what lies beyond?
The truth is, the industry isn’t stopping at 800V. Engineers and manufacturers are already exploring the next frontier—1000V systems and beyond. These higher-voltage systems could potentially reduce charging times to mere minutes, making the “fill-up and go” experience of traditional gas stations a reality for EVs. But with great power comes great responsibility, and these systems will require even more advanced infrastructure and safety measures.
Another exciting development is the concept of modular multi-voltage systems. Imagine a car that can switch between different voltage levels based on the charging station available. This flexibility could revolutionize the way we think about EV charging, making it easier for drivers to find a compatible station no matter where they are.
Market Trends and Manufacturer Adoption
The shift from 400V to 800V is more than just a technological upgrade—it’s a market trend that’s shaping the entire EV industry. Manufacturers are quickly jumping on the 800V bandwagon, and for good reason.
Porsche, Hyundai, and Lucid are already leading the pack with their 800V models, but they’re not alone. Other manufacturers, like Ford, Mercedes-Benz, and Volvo, have also announced plans to adopt 800V systems in their future models. This shift isn’t just about staying competitive; it’s about setting a new standard for what’s possible in the EV world.
But it’s not all smooth sailing. The transition to 800V and beyond isn’t just about building new cars—it’s about creating the infrastructure to support them. That means more high-powered charging stations, more robust electrical grids, and a whole lot of investment. It’s a big challenge, but one that the industry is ready to take on.
Infrastructure Development: Building the Future
Speaking of infrastructure, let’s talk about what it’s going to take to make all of this a reality.
Right now, most public charging stations are designed for 400V systems. Sure, you can find 800V stations if you look hard enough, but they’re few and far between. To support the growing number of 800V vehicles—and prepare for the next generation of even higher-voltage systems—we need a major infrastructure overhaul.
This isn’t just about adding more charging stations; it’s about upgrading the ones we already have. High-powered stations capable of delivering 800V or more will require thicker cables, advanced cooling systems, and more robust electrical grids. It’s a massive undertaking, but one that’s necessary if we want to keep up with the pace of EV innovation.
The good news? Governments, utilities, and private companies are already stepping up to the plate. Across the globe, we’re seeing investments in charging infrastructure that will not only support today’s EVs but also future-proof the industry for years to come.
Technical Deep Dive: The Science Behind the Speed
Alright, let’s get a little nerdy for a minute. Why does increasing the voltage make such a big difference in charging speed?
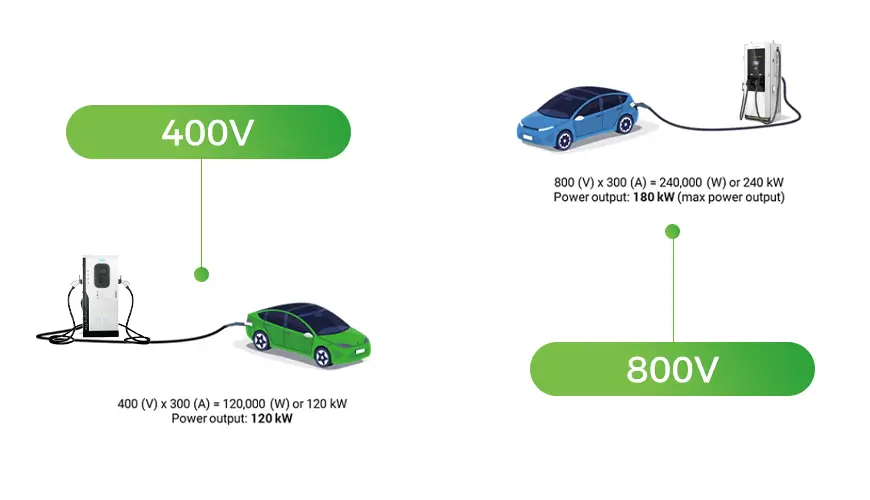
It all comes down to the relationship between voltage, current, and power. In simple terms, power (measured in kilowatts) is the product of voltage and current. By increasing the voltage, you can deliver more power to the vehicle without having to increase the current. This is crucial because higher currents generate more heat, which leads to energy loss and requires thicker, heavier cables.
Let’s take an example: MOREDAY’s 180kW EV charger. When charging a 400V vehicle, the charger delivers 120kW of power. But when charging an 800V vehicle, that same charger can deliver up to 180kW—50% more power with the same current. The result? Faster charging times and a more efficient transfer of energy.
This technical advantage is why 800V systems are so appealing, and it’s also why the industry is looking to push the envelope even further with higher-voltage systems.
Cost-Benefit Analysis: Is It Worth the Investment?
Of course, all of this comes with a price tag. Higher-voltage systems are more expensive to produce, and the infrastructure to support them isn’t cheap either. So, is it really worth the investment?
For manufacturers, the answer is a resounding yes. While the initial costs are higher, the long-term benefits of faster charging times, improved efficiency, and the ability to stay ahead of the competition make it a smart investment.
For consumers, the decision is a bit more nuanced. If you’re someone who values speed and efficiency and is willing to pay a premium for it, then an 800V system (or higher) is definitely worth considering. But if you’re more budget-conscious, a 400V system might be a better fit for now—especially since the infrastructure to support 800V isn’t quite there yet.
Challenges and Solutions: Overcoming the Hurdles
As exciting as all of this is, there are still plenty of challenges to overcome. The biggest hurdle? Infrastructure. Without enough high-powered charging stations, the benefits of 800V and higher systems are limited.
But this isn’t just about adding more stations—it’s about ensuring that our electrical grids can handle the increased demand. High-powered charging stations require more electricity, which can strain local grids, especially in areas with high EV adoption.
The solution? A multi-pronged approach that includes upgrading our electrical infrastructure, deploying more high-powered charging stations, and exploring innovative solutions like mobile charging units and renewable energy integration. It’s a big task, but one that’s absolutely essential if we want to fully realize the potential of higher-voltage EV systems.
Conclusion: Driving Towards the Future
The shift towards 800V battery architecture in EVs marks a significant milestone in the journey towards faster, more efficient electric vehicles. But it’s just the beginning. As the industry continues to innovate, we can expect to see even higher-voltage systems, smarter charging infrastructure, and more advanced technologies that will make EVs more accessible and practical for everyone.What affects the performance of electric vehicle batteries?
MOREDAY is proud to be at the forefront of this revolution, helping to pave the way for a future where electric vehicles aren’t just an alternative—they’re the standard. The road ahead is full of challenges, but with the right investments, collaborations, and innovations, the future of EV charging looks brighter than ever.
FAQ`s.
Q1: What’s the difference between 400V and 800V EV charging?
A1:400V systems are the current standard, offering widespread compatibility but slower charging speeds. 800V systems, on the other hand, offer faster charging and greater efficiency but require more advanced infrastructure.
Q2: Are there any 800V charging stations available now?
A2: Yes, but they’re still relatively rare. Most public charging stations are designed for 400V systems, though 800V stations are becoming more common as more 800V EVs hit the market.
Q3: Will 1000V systems be available soon?
A3: It’s possible! While 800V is currently cutting-edge, the industry is already exploring higher-voltage systems, like 1000V, that could reduce charging times even further.
Q4: Is it worth buying an 800V EV now?
A4: It depends on your priorities. If you value faster charging and are willing to pay a premium, an 800V EV could be a great investment. However, if budget is a concern, a 400V EV might be a better fit until the infrastructure catches up.
Q5: How does MOREDAY contribute to the future of EV charging?
A5: MOREDAY is a leader in developing advanced charging solutions that are compatible with both 400V and 800V systems. We’re also investing in future-proof technologies to support the next generation of EVs.
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.