Introduction
I
n the fast-evolving world of electric vehicles (EVs), power batteries are the heartbeat that keeps the wheels turning. With the global push toward sustainability and reducing carbon emissions, these batteries have become more important than ever. But not all automotive batteries are created equal. In fact, there are several types, each with its own set of strengths, weaknesses, and ideal applications. So, let’s dive into the fascinating world of automotive power batteries, breaking down the main types and what makes each one tick.
What Are EV Power Batteries?
Before we get into the different types, let’s get on the same page about what we mean by “automotive power batteries.” In the simplest terms, these are batteries specifically designed to power electric vehicles. They store and deliver the energy needed to propel the vehicle, powering everything from the electric motor to the vehicle’s electronics.
Unlike the regular car batteries you’re used to, which are primarily for starting the engine and powering small electronics, automotive power batteries are much more complex. They need to store a lot more energy, deliver it efficiently, and do so safely and reliably over many years. This is why the type of battery inside an electric car matters so much. It’s like the difference between a simple AA battery and a high-capacity rechargeable battery—they’re both batteries, but they’re designed for very different purposes.
The Main Types of EV Power Batteries
Power batteries mainly include lead-acid batteries, nickel metal hydride batteries, lithium-ion batteries, zinc-air batteries, supercapacitors, etc.
Lead-acid Battery classification
Lead-acid battery classification: Lead-acid battery refers to a battery that uses lead dioxide as the positive active material, sponge lead as the negative active material, and sulfuric acid solution as the electrolyte. Acid batteries are mainly used in low-speed electric vehicles.
Maintenance-free lead-acid battery: Due to its structural advantages, the consumption of electrolyte in maintenance-free lead-acid battery is very small, and distilled water is basically not needed during its service life. It has the characteristics of vibration resistance, high temperature resistance, small size and low self-discharge. The service life is generally twice that of ordinary lead-acid batteries. There are also two types of maintenance-free lead-acid batteries on the market: the first type is to add electrolyte once when purchased, and no additional electrolyte is needed during use; the other type is that the battery itself has been filled with electrolyte and sealed when it leaves the factory, and the user cannot add additional electrolyte at all.
Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery: Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery does not need to be maintained by adding acid or water during use. The battery is a sealed structure, will not leak acid, and will not discharge acid mist. There is an overflow valve (also called a safety valve) on the battery cover. Its function is that when the amount of gas inside the battery exceeds a certain value, that is, when the internal air pressure of the battery rises to a certain value, the overflow valve automatically opens to discharge gas, and then automatically closes to prevent air from entering the battery. Valve-regulated sealed lead-acid batteries are divided into two types: glass fiber (AGM) and colloid (GEL) batteries. AGM batteries use adsorbed glass fiber cotton as a diaphragm, and the electrolyte is adsorbed in the plates and diaphragms. There is no flowing electrolyte in the battery. The battery can be placed vertically or horizontally. GEL batteries use silicon dioxide (SiO2) as a coagulant, and the electrolyte is adsorbed in the plates and colloids. Generally, they are placed vertically. Unless otherwise specified, they all refer to AGM batteries. The power battery used in electric vehicles is generally a valve-regulated sealed lead-acid battery.
Lead-acid Battery Structure
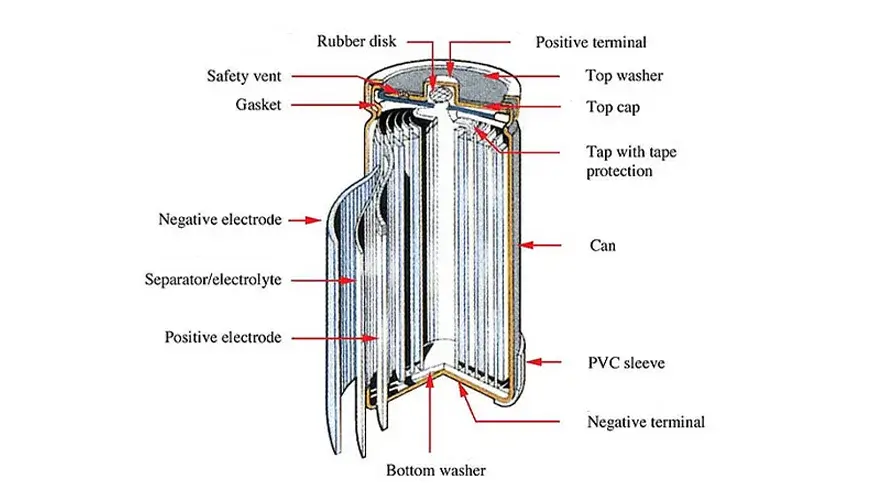
The basic structure of a lead-acid battery is shown in the figure below. It consists of positive and negative plates, separators, electrolyte, overflow valve, shell and other parts.
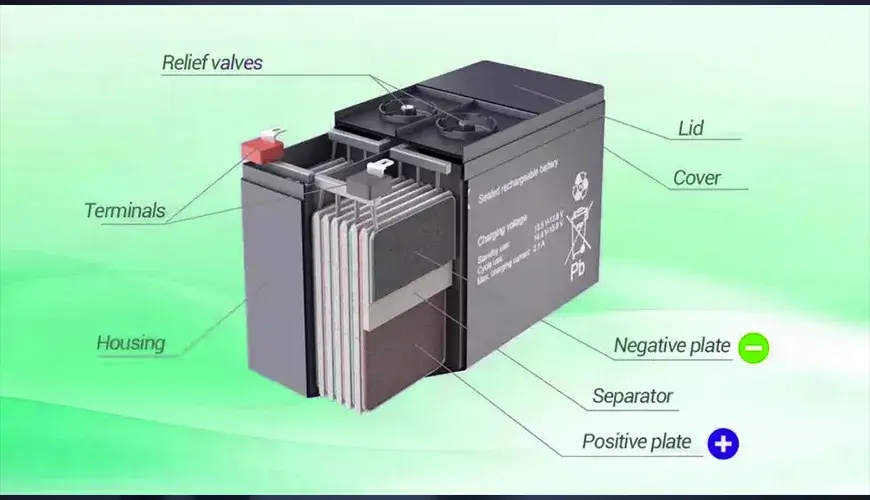

Plate: The core component of a lead-acid battery. The active material on the positive plate is lead dioxide, and the active material on the negative plate is sponge-like pure lead.
Separator: Isolates the positive and negative plates to prevent short circuits. As a carrier of electrolyte, it can absorb a large amount of electrolyte and promote the good diffusion of ions.
Electrolyte: It is made of distilled water and pure sulfuric acid in a certain proportion. Its main function is to participate in electrochemical reactions and it is one of the active substances in lead-acid batteries.
Overflow valve: Located on the top of the battery, it plays a role in safety, sealing, and explosion-proof.
Working Principle of Lead-acid Battery
Working principle of lead-acid battery: When using lead-acid battery, the process of converting chemical energy into electrical energy is called discharge. After use, direct current is used to carry out chemical reaction in the battery, converting electrical energy into chemical energy and storing it. This storage process is called charging. Lead-acid battery is an acid battery, and its chemical reaction formula is: PbO+H2SO4→PbSO4+H2O.
Cathode reduction reaction: Connect the lead plate to the positive and negative electrodes of the DC power supply for charging and electrolysis.
PbSO₄+2e¯→Pb+SO₄²¯
Oxidation reaction at the anode:
PbSO₄+2H₂O→PbO₂+2e-+4H++SO₄²¯
The total reaction during charging: 2PbSO₄+2H₂O→Pb+PbO₂+2H₂SO₄
Oxidation reaction at the cathode of the battery: As the current passes through, PbSO₄ turns into fluffy metallic lead at the cathode and dark brown lead dioxide at the anode, and H₂SO₄ is generated in the solution. Pb→Pb2++2e-
Reduction reaction at the anode: PbO₂+4H++2e-→Pb2++2H₂O Due to the presence of sulfuric acid, Pb2+ also immediately generates PbSO₄
The overall reaction during discharge: Pb+PbO₂+2H₂SO₄→2PbSO₄+2H₂O
Note: When the battery is charged, as the battery terminal voltage increases, water begins to be electrolyzed. When the single cell voltage reaches about 2.39V, the electrolysis of water cannot be ignored. The anode gives electrons and the cathode receives electrons, thus forming a loop current. The higher the terminal voltage, the more intense the electrolysis of water. At this time, most of the charged charges participate in the electrolysis of water, and very few active substances are formed.
Requirements for Lead-acid Batteries in Electric Vehicles
1. Appearance: When visually inspecting the appearance of the battery, the outer shell must not be deformed or cracked, the surface must be dry and free of acid, and the markings must be clear and correct.
2. Polarity: When checking the battery polarity with a voltmeter, the battery polarity should be consistent with the polarity symbol on the mark.
3. Dimensions and quality: The dimensions and quality of the battery should comply with relevant standards.
4. Terminals: The location of the terminals and the specific requirements for their appearance, structure, etc. shall be determined by the user and the manufacturer through consultation.
5. 3H rate rated capacity: When the battery is tested as required, the first capacity should not be less than 90% of the rated value; the battery should reach the rated value on or before the 10th capacity test, and the final discharge capacity should not be higher than 110% of the rated value provided by the company.
6. High current discharge: The fully charged battery is kept at rest for 5 hours in an environment with a temperature of 209°C ± 5°C, and then discharged at a constant current of 313A until the voltage of the single battery reaches 1.5V. The discharge time should be no less than 40 minutes. The fully charged battery is kept at rest for 5 hours in an environment with a temperature of 20°C ± 5°C, and then discharged at a constant current of 913A for 3 minutes. The voltage of the single battery should not be less than 1.4V.
7. Fast charging capability: When the battery is discharged according to the prescribed method, the charging capacity should not be less than 70% of the rated value.
Additional requirements for lead-acid batteries
1. -20℃ low temperature discharge: The fully charged battery is placed in an environment with a temperature of -20℃±2℃ for 20h, and is continuously discharged at a current of 613A in this environment until the voltage of the single battery is 1.4V. The discharge time should be no less than 5min; The fully charged battery is placed in an environment with a temperature of -20℃±2℃ for 20h, and is continuously discharged at a current of 13A in this environment until the voltage of the single battery is 1.4V. The capacity should not be less than 55% of the rated value.
2. Sealing reaction efficiency: For valve-regulated sealed lead-acid batteries, the sealing reaction efficiency shall not be less than 90% when tested according to the prescribed method.
3. Charge retention capacity: When the battery is tested according to the prescribed method, its room temperature capacity should not be less than 85% of the capacity before storage; the high temperature capacity should not be less than 70% of the capacity before storage.
4. Cycle endurance: When the battery is tested according to the prescribed method, when the battery capacity drops to 80% of the rated value, the number of cycles should be no less than 400 times.
5. Safety: After the battery is fully charged according to the prescribed method, charge it continuously for 5 hours at a current of 0.7l3 (A), and then visually inspect the appearance of the battery. The outer shell must not have leakage, cracks or other abnormal phenomena.
6. Water loss: For maintenance-free lead-acid batteries, when tested according to the prescribed method, the water loss should not exceed 3g/(Ah) based on the rated capacity.
7. Vibration resistance: The battery is tested according to the prescribed method. During the test, the battery discharge voltage should be normal. After the test, the battery should be checked for mechanical damage and electrolyte leakage.
Nickel Metal Hydride Battery
Definition and classification of nickel metal hydride batteries
Nickel metal hydride batteries, also known as nickel-metal hydride batteries, refer to batteries that use nickel oxide as the positive electrode, a hydrogen storage alloy that can absorb and release hydrogen as the negative electrode, and potassium hydroxide as the electrolyte.
Nickel metal hydride batteries are widely used in hybrid electric vehicles.
Nickel metal hydride batteries for electric vehicles can be divided into two types: square and cylindrical.
Structure of nickel metal hydride battery
The structure of a cylindrical nickel metal hydride battery is shown in the figure below, which is mainly composed of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separation layer, a shell, an electrolyte, etc.
The positive electrode of the nickel metal hydride battery is the active material nickel hydroxide, the negative electrode is the hydrogen storage alloy, the separation layer is the diaphragm paper, potassium hydroxide is used as the electrolyte, and there is a separation layer between the positive and negative electrodes, which together form a nickel metal hydride single cell. Under the catalytic action of metal platinum, the reversible reaction of charging and discharging is completed.
In cylindrical batteries, the positive and negative electrodes are separated by separator paper, rolled together and then sealed in a metal casing.
In square batteries, the positive and negative electrodes are separated by separator paper, stacked into layers and sealed in the casing.
The basic unit of nickel-metal hydride batteries for electric vehicles is a single cell, which is combined into nickel-metal hydride battery assemblies with different voltages and different charges according to usage requirements, as shown in the figure below.
Working principle of nickel metal hydride battery: nickel metal hydride battery is a device that directly converts the energy generated by the chemical reaction of substances into electrical energy. The performance characteristics of nickel metal hydride battery mainly depend on the electrode reaction of its own system.
Electrochemical reaction of positive and negative electrodes during charging: Ni(OH)2-e-+OH-→NiOOH+H2O2MH+2e-→2M-+H2
Electrochemical reaction of positive and negative electrodes during discharge: NiOOH+H2O+e-→Ni(OH)2+OH-2M-+H2→2MH+2e-
Requirements for Nickel Metal Hydride Batteries

Requirements for single battery:
1. Appearance: In good light conditions, visually inspect the appearance of the single battery. The shell must not be deformed or cracked, and the surface must be flat, dry, free of alkali marks, dirt, and clear.
2. Polarity: When checking the polarity of the battery with a voltmeter, the battery polarity should be consistent with the polarity symbol on the mark.
3. Dimensions and quality: The dimensions and quality of the single battery should meet the technical requirements provided by the manufacturer.
4. Room temperature discharge capacity: When the single battery is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than the rated capacity and should not exceed 110% of the rated capacity. At the same time, the initial capacity range of all test objects should not be greater than 5% of the average initial capacity.
Requirements for battery modules:
1. Appearance: In good light conditions, use visual inspection to check the appearance of the battery module. The appearance should not be deformed or cracked, the surface should be flat and dry, without external injuries, and the arrangement should be neat, the connection should be reliable, and the markings should be clear.
2. Polarity: When checking the polarity of the battery module with a voltmeter, the battery polarity should be consistent with the polarity symbol of the mark.
3. Dimensions and quality: The dimensions and quality of the battery module should meet the technical conditions provided by the manufacturer.
4. Room temperature discharge capacity: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than the rated value and should not exceed 110% of the rated capacity. At the same time, the initial capacity range of all test objects should not be greater than 7% of the average initial capacity.
5. Room temperature rate discharge capacity: Test according to the battery type provided by the manufacturer. When the high-energy battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than 90% of the initial capacity; when the high-power battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than 80% of the initial capacity.
6. Room temperature rate charging performance: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than 80% of the initial capacity.
7. Low temperature discharge capacity: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than 80% of the initial capacity.
8. High temperature discharge capacity: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its discharge capacity should not be less than 90% of the initial capacity.
9. Charge retention and capacity recovery capability: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, its room temperature charge retention rate should not be less than 85% of the initial capacity, the high temperature charge retention rate should not be less than 70% of the initial capacity, and the capacity recovery should not be less than 95% of the initial capacity.
10. Vibration resistance: When the battery module is subjected to vibration resistance test according to the prescribed method, sharp change of discharge current, abnormal voltage, deformation of battery shell, electrolyte overflow and other phenomena are not allowed, and the connection should be reliable and the structure should be intact.
11. Storage: When the battery module is tested according to the prescribed method, the capacity recovery should not be less than 90% of the initial capacity.
12. Safety: When the battery module is subjected to short circuit, over-discharge, over-charge, heating, puncture, extrusion and other tests according to the prescribed methods, it should not explode, catch fire or leak.
Conclusion
This article details several types of electric vehicle powertrains. We will focus on one type of battery, which is also the most commonly used type of battery on the market: lithium-ion batteries.
Continue viewing: Knowledge about EV Power Lithium-ion Batteries
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.








