Introduction
A
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more common on roads around the world, one thing every EV driver quickly realizes is that not all charging connectors are the same. Much like how different phones have their own types of charging cables, EVs come with a variety of charging connectors. In this guide, we’ll break down the different types of EV charging connectors used across the globe, their pros and cons, and which ones are best suited for your needs. Whether you’re a new EV owner, an installer, or just curious about the technology, you’ll find everything you need to know here.
1. Understanding the Basics: AC vs. DC Charging
Before we dive into connector types, let’s first talk about the difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) charging. Every EV can use both, but the method of delivery makes a big difference in charging time.
AC Charging: This is the more common type of charging, and it happens at slower speeds. When you plug your car into an AC charger, the power from the grid goes through the car’s onboard charger, which converts it into DC power to store in the battery. AC charging is often used for Level 1 (home) or Level 2 (public) charging, and it’s ideal for everyday use when time isn’t a pressing issue.
DC Fast Charging: If you need a quick top-up, DC fast charging is your best friend. Here, the conversion happens at the charging station, so the power goes directly into your EV’s battery. Since it skips the onboard converter, DC fast charging is much quicker but requires specialized equipment and connectors.
Now that we’ve cleared that up, let’s move on to the connector types!
2. Types of EV Charging Connectors: A Global Breakdown
Here’s where things get a little more complicated because connector types can vary depending on where you live. But don’t worry—we’re here to simplify it for you.
North America: SAE J1772 (Type 1) and Tesla NACS

SAE J1772 (Type 1): If you live in North America, chances are your EV uses the J1772 plug, also called Type 1. This is the most common connector for AC charging and works with both Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. While it’s reliable, it only supports single-phase charging, meaning it’s a bit slower than some other options out there. But don’t worry—it still gets the job done for everyday charging needs.
Advantages:
- Easy to find across North America
- Compatible with most non-Tesla EVs
- Can be adapted for use with Tesla vehicles
Disadvantages:
- Only supports single-phase AC charging
- Lacks an automatic locking mechanism
Tesla NACS (North American Charging Standard): Tesla has its own proprietary plug in North America. It’s sleek, compact, and supports both AC and DC fast charging (previously called Tesla Supercharger). Recently, Tesla opened up this connector to other manufacturers, so we may see it more widely used in the future.
Advantages:
- Can handle high power, up to 250 kW
- Compatible with Tesla Supercharger network
- Smaller and easier to handle than other connectors
Disadvantages:
- Proprietary to Tesla, though expanding availability
- Not as widely compatible with non-Tesla chargers without an adapter
Europe: Mennekes (Type 2) and CCS Combo 2
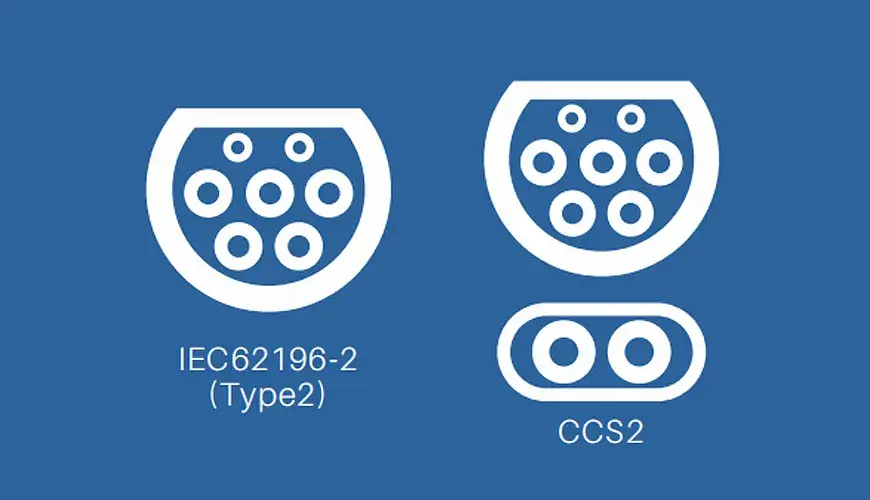
Mennekes (Type 2): Europe uses the Type 2 connector, also known as Mennekes. This versatile plug works with both single-phase and three-phase AC charging, making it faster and more efficient than its North American counterpart. Plus, it features an automatic locking mechanism, so once it’s plugged in, it stays put.
Advantages:
- Supports both single- and three-phase charging
- Widely used in Europe and other regions
- Automatic locking mechanism for added safety
Disadvantages:
- Slightly bulkier than Type 1
- Requires an adapter for Tesla Superchargers in some cases
CCS Combo 2: If you’re in Europe and looking for fast charging, you’ll likely use the CCS Combo 2. This connector combines the Mennekes Type 2 AC plug with two additional pins for DC fast charging. With CCS 2, you get the best of both worlds—one plug for both AC and DC charging.
Advantages:
- One port for both AC and DC fast charging
- Compatible with most European EVs
- High power capacity, up to 360 kW
Disadvantages:
- Larger and heavier than other connectors
- Still not as fast as CHAdeMO for some vehicles
Asia: CHAdeMO and GB/T
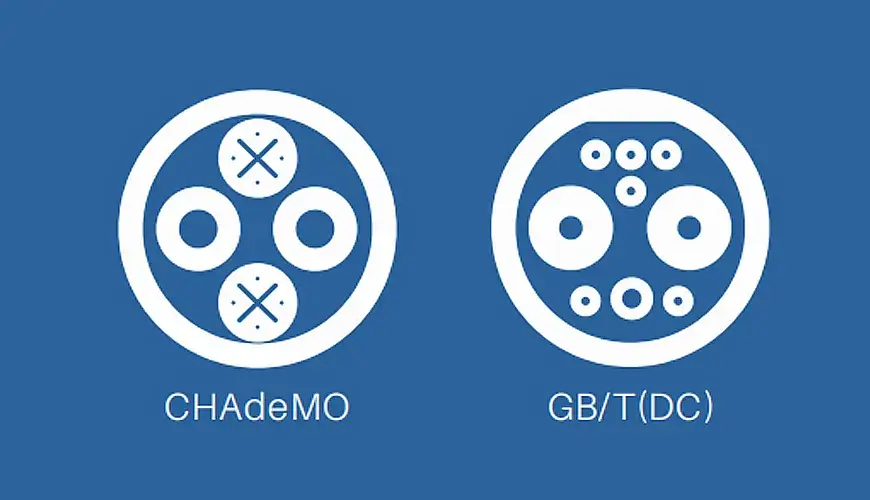
CHAdeMO: This DC fast-charging connector was developed in Japan and is used in older Nissan Leafs and other Japanese EVs. While it can handle high power, it’s slowly being phased out in favor of the CCS standard. However, it’s still the go-to in Japan, and some CHAdeMO stations can deliver up to 400 kW with liquid cooling.
Advantages:
- High power output, up to 400 kW
- Widely used in Japan
Disadvantages:
- Requires a separate AC charging port
- Losing market share to CCS
GB/T: China’s GB/T connector is the country’s national standard for both AC and DC charging. The AC version supports up to 7.4 kW, while the DC version can deliver up to 237.5 kW. This is the only connector standard used in China, so it’s essential for anyone driving or selling EVs there.
Advantages:
- Standardized for both AC and DC charging in China
- High power output for DC charging
Disadvantages:
- Only compatible within China
- Requires adapters for use outside of China
Global: Tesla (Outside North America)
Tesla Type 2: Outside North America, Tesla models like the Model 3 and Model Y use a modified Type 2 connector for AC and DC charging. The key difference is that this version of the Type 2 has notches to prevent non-Tesla vehicles from using Tesla Superchargers.
Advantages:
- Compatible with European charging infrastructure
- Can handle both AC and DC fast charging
Disadvantages:
- Limited to Tesla vehicles unless using an adapter
3. The Future of Fast Charging: What to Expect?
So, what’s next for EV charging? With technology advancing rapidly, we’re already seeing connectors that can handle enormous power levels. For example, the CHAdeMO and GB/T standards are working together to develop a new connector capable of handling up to 900 kW. That could mean charging your car in just a few minutes!
Additionally, more chargers are being equipped with liquid-cooled cables, which can handle the higher currents required for super-fast charging. As EV adoption grows, we’ll likely see a shift toward standardization—perhaps a world where we only need one type of connector, much like how USB-C has become the go-to charging standard for phones and laptops.
4. EV Charging Connector Compatibility and Safety
Charging your EV isn’t just about convenience—it’s also about safety. Using the wrong connector can lead to slower charging or even damage to your car’s battery. That’s why it’s essential to know which connector is compatible with your EV. Thankfully, most charging stations have built-in safety features like overcurrent protection and temperature control to keep your vehicle and the station safe.
When in doubt, always refer to your EV’s manual or consult with your local charging station provider to make sure you’re using the right connector.
5. Choosing the Right Charging Solution for Your Needs
Now that we’ve gone over the different types of connectors, the big question is: which one is right for you?
For EV Owners: If you own an EV in North America, you’ll likely be using J1772 for daily charging and possibly a Tesla adapter if you drive a non-Tesla vehicle. In Europe, Mennekes Type 2 is your best bet for AC charging, while CCS 2 will get you fast DC charging when you’re in a hurry.
For Installers: Future-proofing is critical! Installing chargers that support both AC and DC charging ensures you can accommodate the broadest range of EVs. Look for stations that offer CCS Combo connectors, as they are compatible with most EVs and provide flexibility for both slow and fast charging.
6. Why MOREDAY is Your Go-To Manufacturer for EV Charging Solutions
At MOREDAY, we pride ourselves on being a leading EV charger manufacturer based in China. We understand the global EV charging landscape and are committed to providing the highest quality charging solutions, whether you need a single AC charger or a full-scale fast-charging network.
With MOREDAY, you get:
- OEM/ODM services tailored to your business needs.
- International certifications ensuring safety and compatibility across the globe.
- Comprehensive technical support, fast delivery, and after-sales guarantees.
If you’re looking for a reliable partner for your EV charging needs, MOREDAY is here to help.
Conclusion
Understanding the various EV charging connector types is crucial, whether you’re a car owner, installer, or policymaker. From J1772 in North America to Mennekes in Europe and GB/T in China, each connector serves its market with specific advantages and limitations. As the EV industry evolves, charging standards will continue to adapt, but staying informed about current technologies can help you make the best choices for your needs.
Related Reading:CCS1 vs CCS2: Understanding the Differences
FAQ`s.
Q1: What’s the difference between AC and DC charging?
A1:AC charging uses your car’s onboard converter, while DC fast charging sends power directly to your car’s battery, making it faster but requiring specialized connectors.
Q2: Can I use a Tesla charger with non-Tesla vehicles?
A2: In some regions, yes! Tesla now provides adapters in North America, and in Europe, Tesla Superchargers can work with other vehicles using the CCS Combo 2 connector.
Q3: Why is CHAdeMO being phased out?
A3: CHAdeMO is losing ground to the CCS standard, which allows for one port for both AC and DC charging, simplifying vehicle design and infrastructure.
Q4: How fast can I charge my car with a CCS Combo connector?
A4: A CCS Combo 2 connector can deliver up to 360 kW, allowing for ultra-fast charging that could recharge most EVs in under 30 minutes.
Q5: Are EV connectors standardized across the globe?
A5: Not quite. Different regions use different standards (e.g., J1772 in North America, Type 2 in Europe), but the trend is moving towards global compatibility, especially with CCS.
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.








