Z
inc-air batteries might not be the first thing that comes to mind when you think of energy storage, but these little powerhouses are quietly making waves in various industries. From hearing aids to electric vehicles, zinc-air batteries have a unique set of features that make them stand out from the crowd. But what exactly are they? How do they work? And why should you care? Let’s dive into the world of zinc-air batteries, explore their inner workings, and uncover the potential they hold for the future.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of how zinc-air batteries work, let’s take a quick trip down memory lane. Zinc-air batteries aren’t exactly new; they’ve been around for quite some time. The concept of using zinc and air to generate electricity dates back to the 19th century, with the first practical zinc-air battery developed in the early 20th century. Over the years, these batteries have evolved, becoming more efficient and reliable, but the basic principle remains the same.
What is a Zinc-air Battery?
Zinc-air battery is a kind of high-efficiency and environmentally friendly battery which uses oxygen in the air as the positive electrode active material. Theoretically, the mass specific energy of zinc-air battery is 340W*h/kg and the volume specific energy is 1050W*h/L, which is the highest among all chemical power sources at present and the actual specific energy is also the highest. Zinc-air battery has stable discharge voltage, long discharge duration, no environmental pollution, low cost, easy to obtain raw materials and simple manufacturing process. It is known as an environmentally friendly new energy for the 21st century and is used in electric buses.
Zinc-air Battery Structure
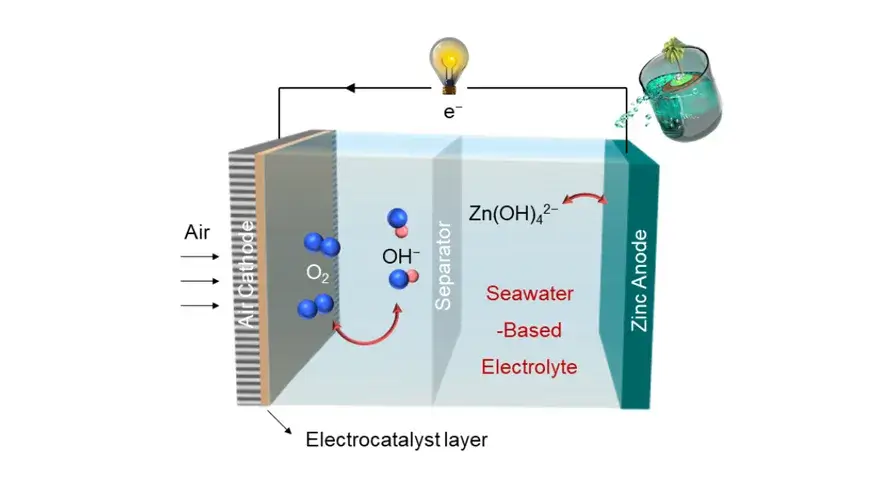
The basic structure of zinc-air battery is shown in the figure below, which mainly consists of anode, cathode, separator, insulation and sealing layer, electrolyte and shell.
The anode is a catalytic carbon that absorbs oxygen from the air.
The cathode is a mixture of zinc powder and electrolyte in a paste form.
The isolation layer is used to isolate the movement of solid powder particles between the two electrodes.
The insulation and sealing layer is made of nylon material.
The electrolyte is a high-concentration potassium hydroxide aqueous solution.
The outer shell is nickel metal, a conductor with good corrosion resistance.
Zinc-air Battery Features
Zinc-air battery is a new type of chemical power source that uses oxygen in the air as the positive active material and metal zinc as the negative active material. Zinc-air battery is a half battery and half fuel cell.
The negative electrode active material is encapsulated inside the battery like zinc-manganese, lead-acid and other batteries, and has the characteristics of batteries. The positive electrode active material comes from the oxygen contained in the air outside the battery, and theoretically has unlimited capacity, which is a typical feature of fuel cells.
Since zinc-air batteries start generating electricity only after coming into contact with air, a new zinc-air battery will not start working unless its sealing tape is torn off. Therefore, zinc-air batteries have a long shelf life.
The Electrochemical Process
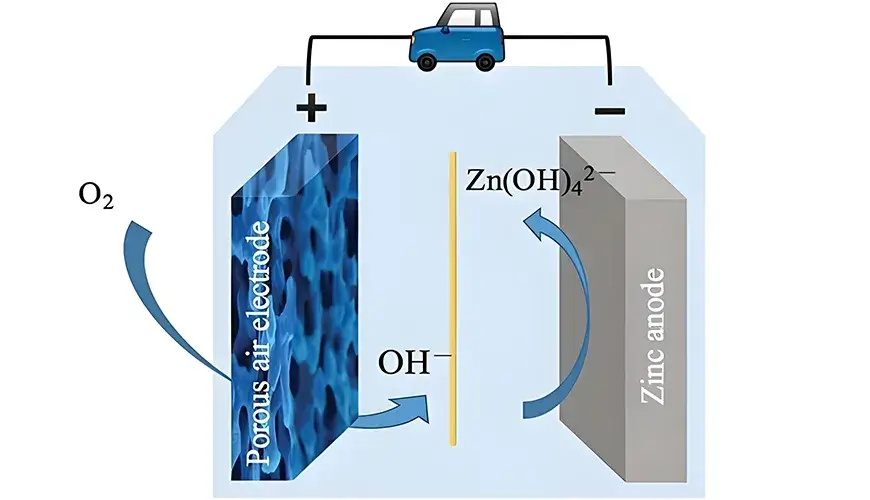
So, how does it all come together? When the battery is in use, oxygen from the air enters the battery through a porous air cathode. This oxygen then reacts with water in the electrolyte to form hydroxide ions. These hydroxide ions travel through the electrolyte to the zinc anode, where they react with the zinc, creating zincate (a type of zinc oxide) and releasing electrons. These electrons then flow through an external circuit—providing power to whatever device the battery is powering—before returning to the air cathode to complete the circuit.
In simpler terms, zinc-air batteries generate electricity by combining zinc and oxygen from the air. It’s like a dance where zinc and oxygen come together to create energy, all facilitated by the electrolyte acting as the dance floor. The beauty of this process is that it’s highly efficient, with minimal waste, making zinc-air batteries an attractive option for various applications.
Zinc-Air Batteries in Action: Current Applications
Despite these challenges, zinc-air batteries are already making a mark in several industries. Let’s take a look at some of the current applications where these batteries are being used.
Hearing Aids
One of the most common uses of zinc-air batteries is in hearing aids. Thanks to their high energy density and small size, zinc-air batteries are perfect for these tiny devices. They can provide a reliable power source for days or even weeks, depending on the hearing aid, without needing to be recharged. Plus, their cost-effectiveness makes them an affordable option for many users.
Electric Vehicles
While zinc-air batteries aren’t yet widespread in the electric vehicle (EV) market, they hold a lot of potential. The high energy density of zinc-air batteries could make them a viable option for extending the range of EVs, especially as research continues to improve their power output and rechargeability. Imagine driving an electric car that can go even further on a single charge, thanks to the power of zinc and air.

Grid Energy Storage
Another exciting application for zinc-air batteries is in grid energy storage. As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources like wind and solar, there’s a growing need for efficient and cost-effective ways to store energy. Zinc-air batteries could provide the solution, offering a way to store excess energy generated during peak production times and release it when it’s needed most. This could help stabilize the grid and ensure a steady supply of power, even when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
The Road Ahead: Future Prospects for Zinc-Air Batteries
So, what does the future hold for zinc-air batteries? While there are still some hurdles to overcome, the prospects are bright.
One area of focus is improving the rechargeability of zinc-air batteries. Researchers are exploring new materials and designs that could make these batteries more durable and capable of being recharged multiple times. There’s also ongoing research into improving the power output of zinc-air batteries, making them more suitable for a wider range of applications.
As these technological improvements are made, the market potential for zinc-air batteries could grow significantly. Their cost-effectiveness, environmental benefits, and high energy density make them an attractive option for a variety of applications, from consumer electronics to large-scale energy storage. As more industries recognize the benefits of zinc-air batteries, we could see them become a more common sight in the market.
Conclusion
In a world where energy storage is becoming increasingly important, zinc-air batteries offer a compelling solution. With their high energy density, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits, these batteries have the potential to power a wide range of applications, from hearing aids to electric vehicles. While there are still some challenges to overcome, the future looks bright for zinc-air batteries as researchers continue to push the boundaries of what this technology can achieve.
So, the next time you hear about battery technology, remember that zinc-air batteries are more than just a buzzword—they’re a powerful tool in the quest for sustainable, efficient, and reliable energy storage.
Derek Ke
Hi, I’m Derek Ke, founder of Moreday.com, an expert in solar-protected electrical products and electric vehicle charging.
Over the past 15 years, we have helped nearly 500 customers (such as farms, residential, industrial, and commercial) in 60 countries solve new energy and green power problems. We aim to share more knowledge about solar power generation and new energy with everyone so that green electricity can enter thousands of households.